
|
Sam Eldin Artificial Intelligence
Business Plan Videos' Scripts© |
|---|
|
AI Business Plan Videos' Scripts Table of Contents: • Introduction • What is an AI Business Plan? • How are we going to develop-build a network of AI Data Centers around the globe? • What is an AI Data Center? • Top AI Data Centers Issues • The Size and The Magnitude of AI Data Centers and Their Building Cost in 2025 • The Total AI Markets are in the $Trillions • What is the cost of cooling AI Data Center in 2025? • Can Computers Hardware Vendors build a AI server without the server box or case? • Massive Heat Dissipation • How Do They Power AI Data Centers? • AI Staff Shortage • AI and Environment Issues • DevOps Support for AI data Centers • Cybersecurity Support for AI Data Centers • AI Data Centers and Heat (Waste Product) Generated • Cybersecurity and Data Center Thermal Attacks • Rapid Growth • Scalability • Data and Privacy • Maintenance • Running Cost • Environment Issues - Revisit • Comply with Regulations • Conclusion • How can these Important Topics and Components be done? • Our Answer is simply - Restructuring • The Size and The Cost • What factors would be considered in bare-metal structure and its performance? • Building Energy Self-Sufficiency AI Data and AI Development Centers • Energy, Cooling and Heat as Reusable Energy • Security • Staffing • DevOps • AI Growth • Data Center Growth • Google, ChatGPT and Our Views on Growth Introduction: Our goal is to present our AI Data and Development Centers Business Plan. Our goals: Our goal(s) in this page is to create short videos presenting this page as our scripts for the videos: We will try to: 1. Keep the length of each video around 10-12 minutes (possible 12 videos) 2. Use Google and ChatGPT definitions and images to present what the world thinks and knows 3. Our Definition in case, we are not in agreement with what world thinks and knows 4. Short examples to make life easier What is an AI Business Plan? We asked ChatGPT: What is an AI Business Plan? It gave us a long definition, which would be summarized as follows: It's a blueprint for integrating AI into the company's operations, products, services, or offerings. Our Definition is: A Business Plan as its name implies is: Step-by-step road map for developing an AI Model-Agent System. How are we going to develop-build a network of AI Data Centers around the Globe? This page (videos scripts) is our attempt to present to both technical and non-technical audience the 2,000 Foot – View of the most important details starting AI Data Center Issues and major obstacles-difficulties. We are also presenting our answers to these hurdles. We do recommend to our audience to have an open mind and see the big picture. Our audience need to understand what we are presenting: • Very complex issues which we are trying to simplify • AI's products and usage are overhyped and we are trying to bring reality to such hype • We need to keep our eyes on the cost and size of AI projects • We are adding intelligence to some AI components like intelligent servers' racks which communicate with servers • We are building a global network of highly specialized AI Data Centers 
World Map The following is a list of countries, and their location in the World Map: Egypt, Saudi Arabia, Gulf Countries, Yamen, Eretria, Somal, Sudan, Oman, Morocco, Chili, Mexico, Puerto Rico, Costo Rica, Australia, Philippine, Baha California What is an AI Data Center? Traditional data centers: These facilities use standard network architectures to handle data transfer across storage, servers and cloud environments. 
Image #1: Data Centers Across the World Looking at Image #1, Data Centers are literally found around the globe. Their capabilities vary significantly. Our Goal is to create a global network of AI Data and Development Centers with futuristic features which the existing data centers lack. 
Image #2: AI Data Centers In Image #2, AI data centers: require high-speed networking and low-latency interconnects because AI workloads involve rapid data movement between processors. An AI data center is a specialized facility designed to support the infrastructure required for artificial intelligence (AI) workloads, such as: • Training machine learning models Running • AI algorithms Storing • Vast amounts of data It differs from traditional data centers in that it's specifically optimized for the high computational demands and data requirements of AI applications. Top AI Data Centers Issues: To make life easier for us and our audiences, we need to list the top issues with AI Data Centers, then we would be covering these issues with explanations and images. We would be presenting our AI Data and Development Centers Solutions which are addressing all the listed issues. The following are the top issues: 1. Massive size 2. The cost of building these AI Data Centers 3. The total market size 4. Massive Energy consumption 5. Powering AI data centers 6. Heat generated 7. Cooling AI Data Centers 8. Shortage of skilled staff 9. Rapid growing 10. Scalability 11. Security 12. Cooling security 13. Data and privacy 14. Complex hardware 15. Maintenance 16. Running cost 17. Environment issues 18. Comply with regulations The Size and The Magnitude of AI Data Centers and Their Building Cost in 2025: 
Image #3: The Stargate Project - Potentially Reaching $500 Billion The Stargate project, a multi-billion dollar AI data center being built by Microsoft and OpenAI, is considered the most expensive AI data center in the world, with an estimated cost exceeding $100 billion, and potentially reaching $500 billion for the entire campus. This massive undertaking aims to develop a new generation of AI supercomputers for future AI models and is scheduled to begin coming online in 2028. What is the cost of building AI Data Center in 2025? Building a new AI data center in 2025 can cost anywhere from $10 million for a small-scale facility to over $500 million for large-scale projects, with individual large tech companies such as Meta (with its $50 billion Louisiana facility) and Microsoft making massive, multi-billion dollar investments in infrastructure. The final cost depends on the size and processing power required, with high-performance Graphics Processing Unit (GPUs), specialized AI chips, and extensive electrical and cooling infrastructure being major expense drivers. Building an AI data center in 2025 can cost anywhere from $5 million to $500 million or more, depending on the scale and sophistication of the infrastructure. Key drivers of costs include hardware Graphics Processing Unit (GPUs), Tensor Processing Unit (TPU), etc., land and building construction, power and cooling systems, networking, software tools, and ongoing operational expenses. For large-scale or highly specialized AI workloads, the cost of the facility and its operation could be quite substantial. What is the annual cost of running an AI data Center in 2025? There's no single annual cost for running an AI data center in 2025, as expenses vary greatly by scale and location, but factors like hardware, electricity, cooling, and personnel are significant, with some large facilities potentially costing billions in operations alone. For example, one engineer's 2024 estimate for a 100,000-accelerator data center projected annual electricity costs of $44 billion, while a general estimate for a large data center's annual operation is $10 to $25 million. Rule of Thumb for AI Data Centers (2025): • Ongoing operational costs Approximately 20% - 30% of total build cost annually • Example: If a data center costs $100M to build, expect to spend $20M to $30M per year to operate. "Houston, we have a problem": The iconic line "Houston, we have a problem" was popularized by the movie Apollo 13. Our Views: "AI Data Centers, we have a problem." In short, AI Centers are: • Very expensive to build - in the $Billions • Very expensive to run-maintain - in the $Billions • AI Data and development Centers are the future The Total AI Markets are in the $Trillions: How much the Gulf states and Saudi Arabia are willing to spend on AI Projects? Saudi Arabia committed $600 billion over four years, while Qatar earmarked $1.2 trillion and the UAE said it would add $200 billion to an existing $1.4 trillion plan to develop artificial intelligence. How much US is willing to spend on AI Projects? Total US spending on artificial intelligence (AI) projects in 2025 is projected to reach hundreds of billions of dollars, with the vast majority coming from private industry. The federal government is also substantially increasing its investment, though on a much smaller scale. How much Europe is spending on AI Projects in 2025? The action plan involves investing $235 billion towards supporting development of AI in the EU, with a focus on enhancing its AI infrastructure, increasing data access, developing advanced algorithms, fostering adoption in strategic sectors, and facilitating compliance with the EU AI Act. How much China is spending on AI Projects in 2025? China's AI investment could reach $98 billion in 2025, a 48% growth. Government funding will dominate at $56 billion, while internet companies contribute $24 billion to AI. How much will the world spend on AI in 2025? Worldwide spending on AI is forecast to total nearly $1.5 trillion in 2025 according to Gartner, Inc. a business and technology insights company. What is the cost of cooling AI Data Center in 2025? The exact cost of cooling an AI data center in 2025 varies significantly by scale and technology, but it's a substantial operational expense. For example, cooling can consume up to 40% of a data center's total energy budget, with some smaller-scale AI hardware requiring an estimated $10,000-$20,000 per month for cooling alone. Liquid cooling technologies offer significant energy savings compared to air cooling but require higher upfront costs, while new geothermal solutions are being explored to reduce this significant energy demand. What are the types of the cooling methods used in AI Data Centers? Data centers primarily use: • Air cooling • Liquid cooling systems • Evaporative cooling 
Image #4: Cooling AI Data Centers Image #4 presents the use of air cooling and liquid cooling and to manage heat, with air-based systems often using CRAC (Computer Room Air Conditioner) units and sophisticated airflow management techniques like hot and cold aisles. Liquid cooling, increasingly used for higher density environments, involves direct-to-chip or immersion cooling using fluids to more efficiently transfer heat from servers to the environment. Other methods include evaporative cooling, which uses water to cool air, and advanced rack-level solutions for targeted heat removal. Servers' Racks and Wiring: AI data center server racks face extreme challenges compared to traditional data centers due to the high-density, power-hungry nature of modern AI hardware, such as GPUs. This creates significant issues in cooling, power distribution, cable management, physical rack infrastructure, and overall operational efficiency. AI data centers face significant wiring issues due to their unprecedented power and data demands, which exceed the infrastructure of traditional data centers. AI servers, with dense clusters of GPUs and other high-performance hardware, require exponentially more fiber cabling and specialized power delivery. 
Image #5: AI Data Centers Server's Racks Image #5 shows AI Data Centers' racks and the enclosure to control the heat and cooling air or even liquids. 
Image #6: AI Data Centers Wiring Image #6 shows AI Data Centers wiring issues and the overwhelming size of these clusters of wires. Servers' Box, System Unit, or Computer Case: 
Image #7: Servers' Box, System Unit, or Computer Case Servers' Box, system unit, or computer case is the technical term for the main part of a personal computer that contains the processing components. It is the most common and general term for the box that holds the computer's internal hardware. Can Computers Hardware Vendors build a AI server without the server box or case? Yes, computer hardware vendors can and do build AI server hardware without a traditional server box or case. In the context of large-scale data centers, the standard metal chassis is often replaced with an "open frame" or "open rack" design. These specialized structures are built to house a much higher density of computing components than standard servers. 
Image #8: Server without the Server Box or Case Massive Heat Dissipation: The most powerful AI servers use multiple high-wattage GPUs, CPUs, and other components, which generate a tremendous amount of heat. An open frame allows for unobstructed, efficient airflow, which is critical for cooling these powerful components. Enclosed cases would trap this heat, potentially causing the hardware to overheat. How Do They Power AI Data Centers? AI data centers are powered by high-capacity electrical grids, requiring sites near robust infrastructure to access large volumes of electricity. This power runs through complex electrical distribution systems to servers and other equipment. Because AI training uses enormous computational resources, the primary power source for these centers is the public utility grid, though some companies explore building their own solar and wind farms to provide clean energy. 
Image #9: Powering AI Data Centers Image #9: shows the power generating plans needed to supply power to AI data Centers. AI Staff Shortage: An AI staff shortage exists due to the rapidly accelerating demand for AI-skilled professionals outpacing the supply from universities and training programs, coupled with the rapid evolution of AI technology requiring constant skill updates. This talent gap causes significant challenges, including delays in AI implementation, increased hiring costs, missed innovation opportunities, and potential loss of competitiveness. To address this, companies are focusing on upskilling existing employees, broadening hiring strategies, and exploring AI automation to manage workloads. AI and Environment Issues: AI has significant environmental impacts, including a high energy demand and associated carbon emissions from data centers, water usage, and the creation of substantial e-waste from rapidly evolving hardware. DevOps Support for AI data Centers: DevOps support for AI data centers is an advanced, automated, and predictive approach to managing the massive, complex infrastructure that powers artificial intelligence. It goes beyond traditional data center management by using AI itself to optimize performance, handle incidents, and manage costs. This specialized DevOps incorporates Artificial Intelligence for IT Operations (AIOps) to handle the unique challenges of AI workloads. ChatGPT's Answer: Providing DevOps support for AI data centers involves managing infrastructure, automation, monitoring, deployment pipelines, and ensuring high availability and scalability of compute and storage systems required for AI/ML workloads. Cybersecurity Support for AI Data Centers: Cybersecurity support for AI data centers focuses on a multi-layered approach, incorporating advanced threat detection, robust hardware and software security, data protection, and integrated physical and cyber defenses. Key strategies include using AI-powered tools to detect and respond to incidents, securing the data center supply chain, encrypting all data, implementing zero trust principles, and ensuring the physical security of hardware and access points. Additionally, managing geopolitical risks and collaborating with government and industry partners are crucial for a comprehensive security framework. ChatGPT's Answer: As AI data centers become increasingly vital for hosting large-scale machine learning models, sensitive datasets, and high-performance computing infrastructure, their security becomes a critical concern. Cybersecurity support for AI data centers should cover a wide range of technical, operational, and regulatory aspects. AI Data Centers and Heat (Waste Product) Generated: 
Image #10: Computer Chips and Heat Generated Image #10: shows Computer Chips and Heat Generated in AI Data Centers. AI processing generates massive amounts of heat, and for data centers. This heat is traditionally treated as a waste product and expelled. We are proposing the conversion of data centers heat into an asset, improving sustainability and creating new revenue streams. Cybersecurity and Data Center Thermal Attacks: Cybersecurity thermal attacks against AI data centers involve hackers manipulating cooling systems to cause hardware damage, disrupt operations, or exfiltrate data. With the immense heat generated by AI servers, these attacks are becoming a critical threat vector. Data center thermal cyberattacks manipulate computational workloads or compromise cooling systems to create localized hotspots and overheating, degrading server performance, increasing costs, and potentially causing component failure or shutdown. These attacks can be difficult to detect and can exploit vulnerabilities in Data Center Infrastructure Management (DCIM) or power systems. Defenses include enhanced thermal monitoring, advanced anomaly detection, robust security for management systems, and strategic workload placement. Rapid Growth The rapid growth of AI data centers is creating significant issues, and this expansion also has a substantial environmental impact through greenhouse gas emissions and land use, alongside supply chain and workforce bottlenecks. Possible issues are: 1. Massive energy and water consumption 2. Substantial environmental impact 3. Energy consumption and grid strain 4. Water consumption and scarcity 5. Climate and health impacts 6. Supply chain and operational challenges 7. Supply chain and infrastructure constraints 8. Inefficient scaling and forecasting Scalability AI data centers face immense scalability issues driven by the extreme demands of: 1. Generative AI 2 Large language models 3. Putting unprecedented pressure on power grids, cooling systems 4. Strain on their Network infrastructure The key challenge is that AI workloads are far more intensive than traditional computing, requiring a complete rethinking of data center design and operation. Data and Privacy Big Data Issues: Big data refers to data sets so large and complex that traditional data processing software cannot manage them. The Issues of Big Data: 1. Size-Magnitude: The sheer size and quantity of data is massive, often measured in petabytes and zettabytes. Sources include social media, website clickstreams, sensors from IoT (Internet of Things) devices, and financial transactions. 2. Updating: This is the speed at which data is created and needs to be processed. For example, a self-driving car relies on a continuous, real-time flow of data to make instant decisions on the road. 3. Structured and Unstructured: Big data encompasses many different data types and formats. This includes traditional structured data (like a spreadsheet), unstructured data (like images, videos, and text), and semi-structured data (like log files and web pages). 4. Analyzing: Only Machine Learning can truly be able to perform accurate and fast data analysis. 5. Quality and Reliability: Veracity refers to the quality and reliability of the data. With data coming from so many different sources, it can be messy, noisy, and contain errors, requiring careful cleaning and management. 6. Cleaning and Pruning: Data cleaning and data pruning are both processes for improving dataset quality and efficiency, but they address different problems. Data cleaning focuses on fixing specific quality issues within a dataset, while data pruning removes entire portions of the dataset to reduce its size for better performance. 7. Net Value: The ultimate goal of big data is to extract valuable insights that lead to better business decisions. Without a clear purpose, the data is just noise. 8. Data Streaming: Data streaming is the process of continuously transmitting and processing a flow of data, often in real-time, instead of in large, discrete batches. This continuous flow is made up of individual data elements, known as events, that are ordered by time and used to derive immediate insights and take action. Sources include Internet of Things (IoT) devices, sensor readings, web activity logs, and financial transactions How Much Data Is Created Daily? According to the latest estimates from Statista, throughout 2024, approximately 402.74 million terabytes of data are generated daily (equal to approximately 402.74 quintillion bytes - 4.0274 X 10E20), encompassing newly created, captured, copied, and consumed information. Data and Privacy: AI data centers face increased privacy risks due to the massive amounts of sensitive data used for training and the potential for AI models to memorize personal information, leading to breaches and misuse like spear-phishing. Safeguarding data requires implementing strong encryption, strict access controls, and the principle of data minimization, using only necessary data. Ensuring data privacy also involves complying with regulations and being aware of supply chain vulnerabilities. Big data continues its exponential growth, largely fueled by the explosion of Internet of Things (IoT) devices and pervasive digital connectivity, leading to a "new data generation" characterized by unprecedented volumes, velocity, and variety of information. This new era is seeing advancements in AI and cloud computing, enabling organizations to store, process, and extract deeper insights from this massive data. However, the scale of data also presents challenges, emphasizing a need for better data management, a strong focus on data ethics and privacy, and a move towards centralized data solutions and decentralized edge computing for efficient analysis. Maintenance For an AI data center, maintenance is more intensive than a traditional data center due to high-density racks, massive power consumption, and increased heat generation. An effective maintenance program combines automated, AI-driven predictive maintenance with regular manual checks across the following main areas: • Facility - infrastructure • DevOps - hardware and software • Power • Cooling • Networking • Staff • AI management • Secutity Running Cost 
Image #11: AI Data Centers Running Costs Image #11: shows AI Data Centers Running Costs. AI data center running costs are dominated by electricity and hardware, with large-scale facilities potentially costing tens of millions per year to operate. Key expenses include the massive energy consumption for powering servers and cooling systems, which can account for a significant portion of the operational budget. The cost of specialized hardware like GPUs is also a major factor, as is ongoing maintenance, networking, and the need for skilled personnel. Environment Issues - Revisit 
Image #12: AI Data Center Environmental Impact Image #12: shows AI Data Centers Environmental Impact. AI data centers have significant environmental impacts, including massive electricity consumption leading to carbon emissions, heavy water usage for cooling, the generation of electronic waste, and the unsustainable extraction of critical minerals for hardware. This increased demand strains power grids, often relying on fossil fuels, and creates localized air pollution that harms human health, particularly in vulnerable communities. Comply with Regulations To ensure AI data complies with regulations, organizations must adopt a comprehensive strategy that includes: • Strong data governance • Adherence to data privacy laws like the GDPR and CCPA • Implementation of ethical frameworks for responsible AI development and deployment Key steps involve: • Establishing clear policies • Conducting regular audits • Employing automated monitoring and risk assessments for bias • Implementing robust security measures • Training personnel • Building AI governance frameworks to manage data throughout its lifecycle Conclusion 
Image #13: 2,000-foot view of AI Data Centers Image #13: 2,000-foot view of AI Data Centers. We need to select the important topics so we can tackle each one with answers and AI proper approaches. The following are what we consider the big topics: • The Size and Cost • Energy, Cooling and Head Dissipation • Security • Staffing • DevOps • Data and privacy • Growth The Size and Cost: 1. Massive size 2. The cost of building these AI Data Centers 3. The Total AI Markets are in the $Trillions and The total market size 4. Maintenance 5. Running cost Energy, Cooling and Head Dissipation: 1. Massive Energy consumption 2. Powering AI data centers 3. Heat generated 4. Massive Heat Dissipation 5. AI Data Centers and Heat (Waste Product) Generated 6. Cooling them 7. Servers' Racks and Wiring 8. Servers' Box, System Unit, or Computer Case Security: 1. Cybersecurity 2. Cooling security 3. Cybersecurity and Data Center Thermal Attack Staffing: 1. Shortage of skilled staff DevOps: 1. DevOps Support for AI data Centers Data and privacy: 1. ML 2. DevOps 3. AI management 4. AI Data Management Growth: 1. Rapid growing 2. Scalability 3. Complex hardware 4. Environment issues 5. Comply with regulations Quick Summary of our answers to the important topics which we can tackle each one with answers and AI proper approaches.
Important Topics and Quick Summary of Our Answers Table is very much the puzzle which we need to unpuzzle by answering: How can these Important Topics and Components be done? Our Strategies: How to control a chaos situation? • Accepting what you can't change • Focusing on what you can • Establish a clear plan • Prioritize tasks to bring order Our Answer is simply - Restructuring: Restructuring is the act of organizing a company, business, or system in a new way to make it operate more effectively. We need to Restructure the following: • The Size and Cost • Energy, Cooling and Head Dissipation • Security • Staffing • DevOps • Data and privacy • Growth Our main strategy is implementing Vertical and Horizontal processes which are: 1. Vertical = Issues with each unit or component 2. Horizontal = The Number of Units as they are spread horizontally across Vertical - Each Unit: 1. Each Server or equipment produces lots of heat and must be cooled 2. Instead of having servers as boxes, placed in opened racks trays: We should be building the racks to replace the box closure The racks would have motherboards with chips located in these motherboards No more wiring, but the racks would have the hard-connections 3. Racks would have built-in motherboard and wiring 4. Using Robots 5. Rack positioning, size and angle of tilting - for ventilation and easy access - including Robots 6. Ventilation 7. Building cooling systems 8. AI maintenance systems 9. Power supplies and lighting 10. The size of the buildings - the average full-scale data center is around 100,000 square feet 11. Using mirrors to light the building during the day Intelligent Servers Racks: The existing servers' racks are more of a dummy structure and all the wiring passing through and around these server racks. We are looking for rack vendors who would build intelligent servers' racks. These intelligent servers' rack would perform the following: • These servers' racks would be controlled by an AI central management system • They would have all the built-in wiring and connections • They can also communicate with servers' motherboards to: o Help in cooling these motherboards o Reporting any issues with the motherboards • Communicate with the Robots servicing the system Horizontal Issues = The Number of Units as they are spread horizontally across: In a horizontally scaled data center, the various infrastructure components like servers, storage units, and network devices are distributed across multiple racks, cabinets, or even data halls. This creates a distributed system that can handle larger workloads and provide better fault tolerance. We need to restructure AI Data and Development Center and building Energy Self-Sufficiency AI Data and AI Development Centers. We also need to build AI Model-Agent Foundation systems for Businesses and Research Institutions. The main steps of restructuring are: 1. Vertical = eliminate issues with each unit or component 2. Horizontal = the number of Units as they are spread horizontally across the Glob 3. Optimum Size 4. Specialization 5. Automation Using Robots 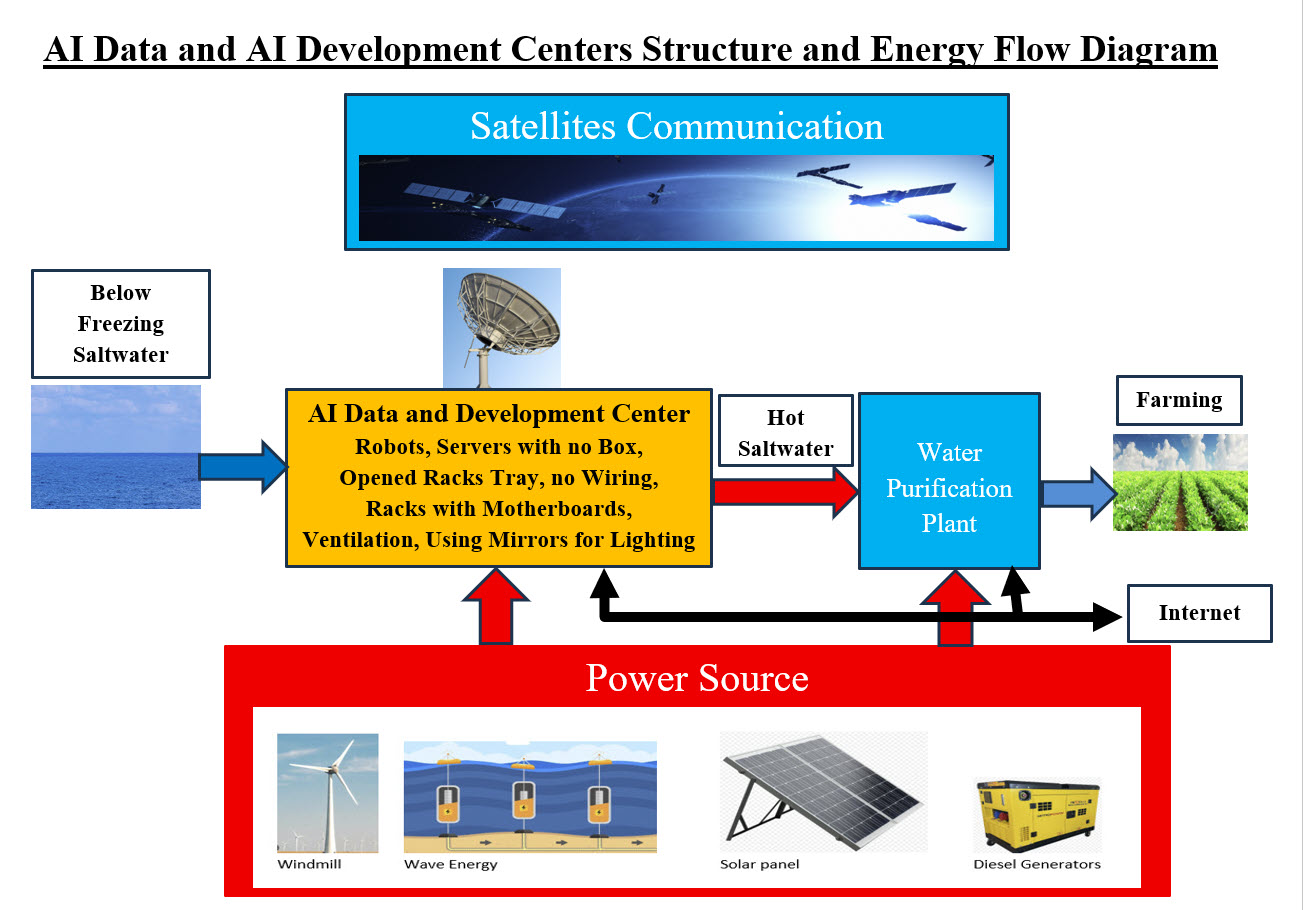
AI Data and AI Development Center Total Picture Diagram We need to present a rough picture of what we are trying to build in simple terms. AI Data and AI Development Centers Structure and Energy Flow Diagram Image shows how we can use the subfreezing saltwater of the oceans or seas to cut the cooling energy bill to zero. How to build a data center and run it by using robots. The heat generated by the center would be used to run Water Purification Plant and protect the environment instead of dumping the hot water back into the ocean or the sea. The fresh water produced has Nemours use. The needed power source would be created from: Windmill + Wave Energy + Solar Panels + Backup and Standby Diesel Generators The Size and The Cost The idea that "bigger is better" is more of personal choice and not a factual, data-based statement and when it comes massive size, the unknown is kind of scary. We need to address the following question: What are the possible issues when it comes to: • AI massive size structure • AI massive size operations • AI massive size Power needed • AI massive size security • AI massive size management We do not want to start a debate on the size, but we would like to present our view of the size of AI structure and operations. Our thinking and approach to size is: Strength in Number "Strength in numbers" is an idiom that means a group of people have more power, influence, or safety than a single individual because they are united and can provide mutual support. The phrase is used to describe the advantage of working together in a group, highlighting that collective efforts are more effective in achieving goals or overcoming challenges. We also like to add the fact that each of member of global network would be able to replace other AI Data Centers in case of issues or problems. We will be developing a global network of high specialized AI Data and Development Centers. The advantage of working together in a group, highlighting that collective efforts are more effective in achieving goals or overcoming challenges. What are the factors which determine the size of each unit or each AI Data and Development Center? We start with basic unit of building AI Data Center, and the basic unit is a running server. What exactly is an AI server? 
AI Running Server Image AI Running Server Image presents the physical servers within an AI Data Centers. In short, there is nothing but racks of running server which must be maintained 24 X 7. The term an AI server refers to servers specifically built to handle the demands of AI workloads. From a component's perspective, AI servers incorporate a variety of discrete hardware elements, including: AI processors, including general-purpose CPUs An AI server is a high-performance computing system specifically designed and optimized to handle the intensive computational demands of artificial intelligence (AI) workloads. Unlike general-purpose servers that handle a variety of tasks sequentially, AI servers are built with specialized hardware and software to process massive datasets and execute complex parallel calculations with maximum speed and efficiency. We are not the experts on servers, but: What factors would be considered in bare-metal structure and its performance? CPU, core, clock speed, registers, cache memory, core memory, bus, chip manufacture support, software support, VM, labor, time, testing and cost. 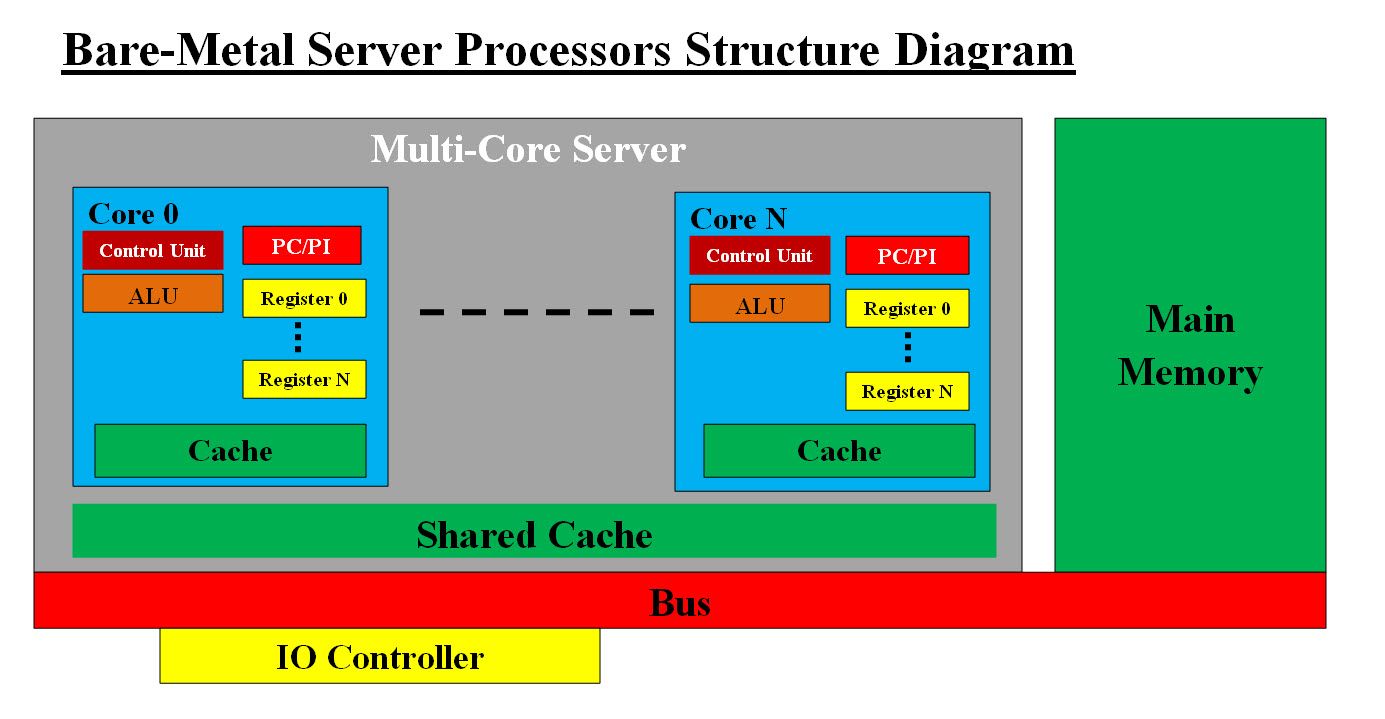
Image #14: Bare-Metal Server's Processor Structure Diagram Image #14: Bare-Metal Server's Processor Structure Diagram presents what we believe a server with multicore processors components should have. In this case, the more the better. For example: Are there bare-metal server with 64 processors more? Yes, bare-metal servers with far more than 64 processors (also referred to as cores or sockets) are available, with options ranging from dual-processor systems that provide 64 cores to servers with multiple sockets that can reach over 200 cores. These high-core-count servers are built with processors like AMD EPYC or Intel Xeon and are designed for demanding workloads like big data analytics, AI/ML, and high-performance computing. Performance Speed: We recommend bare-metal servers with 64 processors more. Each processor would have its own Cache, registers and its own virtual server. Each processor would run independently. We hope that we our recommendation is not dated and there could be more advance bare-metal servers than what we are presenting. Note: Physical or bare-metal server's hardware is quite different than that of other types of computers. Physical server would have Multi-Core processors, IO Controller with multiple hard drive, Error Correction Code (ECC) memory, multiple power supply, threading, parallel computing, redundancies, ..etc. The reason for all these additions is the fact that servers run 24X7 and data loss, damages or slow performance would translate to losing business, customers, ..etc. The Needed Power: What is the energy-electricity needed to run a server with 64 (or more processor) for: 1. One day 2. One month 3. One year ChatGPT said: To estimate the energy and electricity consumption of a server with 64 processors (or more), we need to make some assumptions and perform calculations based on typical power usage for servers. For simplicity, let's assume 200 watts per processor (as an average value). Energy Consumption per Day, Month, and Year: Energy consumption is typically measured in kilowatt-hours (kWh). Here's how we calculate it: Server runs 24 hours a day: 307.2 KWh Assuming 30 days in a month: 9,216 KWh Assuming 365 days in a year: 112,128 KWh What is the average number of servers in good size AI Data Center? It is typically an AI data center houses 2,000 to 5,000 servers. The total energy need by per one year: One Year: 5,000 X 115,000 (rounded 112,128) KWh = 575 MWh rounded to 600 MWH How many Solor Panel needed to produce 600 MWH? You would need about 1,027 solar panels rated at 400W each (with 5 sun hours/day and 80% efficiency) to produce 600 MWh/year. How many windmills are needed to produce 600 MWH per year? A single onshore wind turbine that can handle 2-3 megawatts pumps out about 6 million kilowatt hours (kWh) of electricity each year. Horizontal axis turbines are the most common type seen on onshore and offshore wind farms, usually featuring three blades that look a bit like an airplane propeller. They are highly efficient at generating electricity, with an output of around: 26.1 megawatts (MW) per day X 365 Days = 9,527 MWH Sadly, our Google and ChatGPT searches when it comes to windmills, their number are matching nor sounds correct. 
Image #15: Energy Production Sources for AI Data Centers Image #15: presents our rough draft for how our AI Data Center would be producing its own power and no outside power would be needed. In conclusion: Building Energy Self-Sufficiency AI Data and AI Development Centers We can assume that the size of one AI Data and AI Development Center with 5,000 high-capacity servers can be development with their own windmills and solar panels and no need to any outside energy supply. Energy, Cooling and Heat as Reusable Energy The high energy consumption of AI Data Centers generate extreme heat, creating significant problems for traditional air-cooling systems due to the increased power density of modern AI hardware. A data center produces heat equivalent to almost all of the electrical energy it consumes. For example: • Modern large data centers generating 20-50 MW of heat • Hyperscale data centers producing tens or even hundreds of megawatts This waste heat comes from servers, storage, and networking equipment and is a byproduct of the running servers. Note: CPU limits: CPUs are designed with built-in thermal sensors that will throttle performance or even shut down if they exceed a certain temperature, typically around 90C (194F). However, this is an internal safety limit, not an operational one. Data Center Impact: Large-scale AI data centers can create localized "weather" with air temperatures around heat rejection equipment reaching 140F (60C) in extreme conditions. The first law of thermodynamics, which states that energy cannot be created or destroyed but changes form, with electrical energy primarily converting to heat in a data center. Our Cooling and Heat Reusable Energy: 
Image #16: Fresh Water Creation using Distillation Image #16: presents our rough draft of reusing of servers' heat can be used to Create fresh water using Distillation Our strategy is: Use the subfreezing temperature of Ocean and Seas saltwater to cool the servers. At the same time, we would capture the heat-reuse such heat to create fresh water. Cold Salted seawater in used to cool the servers and the byproduct heat is used to create fresh water. Rainforest Approach: The rainforest approach to creating freshwater is a concept of biomimicry, where technology and conservation efforts are modeled on the natural processes of rainforest ecosystems. Rainforests are powerful water systems that capture, filter, and distribute vast amounts of freshwater, and scientists are replicating these mechanisms on a smaller scale. 
Image #17: Energy, Cooling and Heat as Reusable Energy Image Image #17: presents our rough draft of reusing of servers' heat which can be used to create fresh water using Rainforest Approach. Security The cost of securing AI data centers varies significantly, from hundreds of thousands for small-scale operations to tens of billions for large, hyperscale facilities What is AI Data centers Security Types? 1. Physical Security 2. Cybersecurity 3. Operational Security 4. Data Security 5. Heating-Cooling Security 6. Data Center Thermal Attacks We had covered security in other webpages and also with DevOps system. Staffing Staffing Issues: 1. Shortage of skilled workers for building and operating facilities 2. High turnover rates 3. A widening gap between needed skills and the available workforce 4. Talent gap 5. Retiring workforce 6. Competition with other industries 7. The modern data centers require more diverse and non-technical skills like problem-solving and adaptability Using Robots: Robots are increasingly being used to automate various tasks in data centers, enhancing efficiency, security, and safety while reducing human error. This includes tasks like physical security, environmental monitoring, maintenance, and material handling. In our case, we need Robots which would perform the job of the center staff including physical maintenance of servers and equipment. In short, our AI management, control and maintenance physical asks would be done by Robots. We do need help and also brainstorm what we should be looking for. DevOps We recommend that our audience check the following links and see how we can use DevOps - Infrastructure Support and AI development. DevOps - Infrastructure Support AI Machine Learning Operations (MLOps) Data and Privacy See our Data and Privacy coverage in this page and other links. Growth We asked Google: AI Growth: The answer is: AI is experiencing rapid growth, with the global market projected to reach between $1.68 trillion and $4.8 trillion by 2031-2033, driven by strong private and corporate investment and increasing business adoption. This expansion is fueled by breakthroughs in generative AI and the technology's integration into various industries, although its impact on job growth is still being studied. Investment and market size: • Record investment • Generative AI boom • Market projections Business adoption: • Widespread use • Productivity gains Future trends and outlook: • Increasing sophistication • Potential for economic impact • Continued innovation We asked ChatGPT: AI Growth: Answer: Overview of AI Growth 1. Technological Advancements • Exponential improvement in model capabilities (e.g., language, vision, multi-modal AI). • Real-time reasoning and interaction are becoming more natural (e.g., GPT-4o, Claude, Gemini). • Smaller, more efficient models (e.g., Llama 3, Mistral) are driving adoption on edge devices. 2. Market Growth • The global AI market is expected to surpass $1 trillion by 2030. • Huge investment flows into: o Generative AI (e.g., ChatGPT, Midjourney) o Enterprise AI tools (e.g., Microsoft Copilot, Google Duet) o AI chips (NVIDIA, AMD, etc.) 3. Adoption in Industry • AI is already transforming: o Healthcare (diagnostics, drug discovery) o Finance (fraud detection, trading) o Customer support (chatbots, virtual assistants) o Education (personalized tutoring, content generation) 4. Workforce Impact • Job augmentation in white-collar work is widespread. • Job displacement concerns remain, especially in creative and administrative roles • New roles are emerging: AI ethicists, prompt engineers, AI product managers, etc 5. Ethics and Governance • Governments and coalitions (e.g., EU AI Act, U.S. Executive Order on AI) are stepping in • Topics of concern: bias, surveillance, misinformation, autonomy in military use Our Views on AI Growth and Our Vision: We believe that hardware and processors-CPUs-Core are getting faster by the minutes, while software is still behind. We are technical architects-analysts-PM-developers-testers, therefore our focus for AI is on: How can AI make our technical lives easier? How can AI Growth help IT professionals like us? We believe AI should pick up and move software to chips for faster, efficient and secured software processes, Operating Systems and business packages. AI should make the hardware performs almost all the programming plus builds "Built-in Chips" for utilities, Commons, security, or any redundancies in software development-processes. As for testing, AI should build test scripts, test processes, default testing data and possible standard GUI users' interfaces. In short, replace all the tedious, repetitive and mindless testing processes with an eye on make user interfaces idiotproof. Solving Software Issues: 1. Software is running in slow memory chips and a lot slower IOs 2. We also see motherboards and IOs are lacking intelligence and a big bottleneck for faster processes 3. Not to mention hackers are finding ways into computer system through these software programs and utilities 4. No Intelligent Control Management of DevOps which is the link between hardware, software and the world Solving Data Issues: 1. Lack of universal standards 2. Poor Data analysis system 3. Poor performance by Machine Learning on Big Data 4. The built-in Data is dummy and not an intelligent service We would like AI helps in building and developing the followings: #1. Bare-Metal: 1.1 Multiprocessor CPUs 1.2 Built-in OS Chips 1.3 Built-in OS Chips with security processing 1.4 Built-in Chip Programming 1.5 Built-in Chip utilities Programming 1.6 Faster-cheaper Cache Memory 1.7 Chip-2-Chip Communication-Protocols – eliminate hacking and viruses 1.8 Motherboard embedded Compression and Encryption chips or subsystem 1.9 Intelligent Server Racks – communicate with servers #2. AI Based Foundations for supporting AI Models and Agents – foot soldiers – utilizes #3. Machine Learning – low level business processes with its own chips #4. Intelligent DevOps Support #5. Building Energy Self-Sufficiency AI Data and AI Development Centers We asked Google: AI Data Center Growth: AI data center growth is explosive due: • High-power demands of AI models • Transformation of data center market • Power infrastructure • Surge in construction • Significant investment • Electricity demand • Grid capacity • Grid sustainability • Environment Issues We asked ChatGPT: AI Data Center Growth: Bottom line: • The market for AI optimized data centers is forecast to grow at approximately 25% to 30% • Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) over the next decade • Wth market size potentially increasing many-fold Our Views on AI Data Centers Growth and Our Vision: Our answer to AI Data center growth is we need to learn from history. The Dot-Com Bubble (1995–2002): In the late 1990s, the stock prices of many internet-based companies grew exponentially, only to collapse in 2000-2001. US housing Bubble: The period leading up to the 2008 financial crisis saw a significant rise in real estate prices, which ultimately collapsed. Nuclear power Bubble: A nuclear power bubble refers to the current risk of over-inflated expectations and investment in next-generation nuclear startups before their technology has been commercially proven. While these companies promise a cleaner energy future, concerns persist about high costs, logistical bottlenecks, and regulatory hurdles that could lead to financial losses for unprepared investors. AI Bubble: An AI bubble refers to concerns that the rapid growth in the AI sector is a speculative financial bubble, driven by massive investment and hype, similar to the dot-com bubble of the late 1990s. This theory suggests that a significant number of companies are being valued based on future potential rather than current profits, and that a market correction or burst could occur as investors re-evaluate the technology's actual return on investment. While many believe an AI bubble exists and could lead to a market downturn, others view the massive investment as a necessary and justified technological revolution, though potentially with misdirected investments. |
|---|