

|
Hosting Fundamentals, Costs and Issues |
|---|
|
Hosting Fundamentals, Costs and Issues
Introduction: The goal of this page is to briefly address hosting fundamentals and the costs: The actual cost and the hidden or behind the scenes cost. In a nutshell, hosting is how to access other computers and their resources. Types of Web Hosting:
Hosting levels: Hosting would provide the following levels:
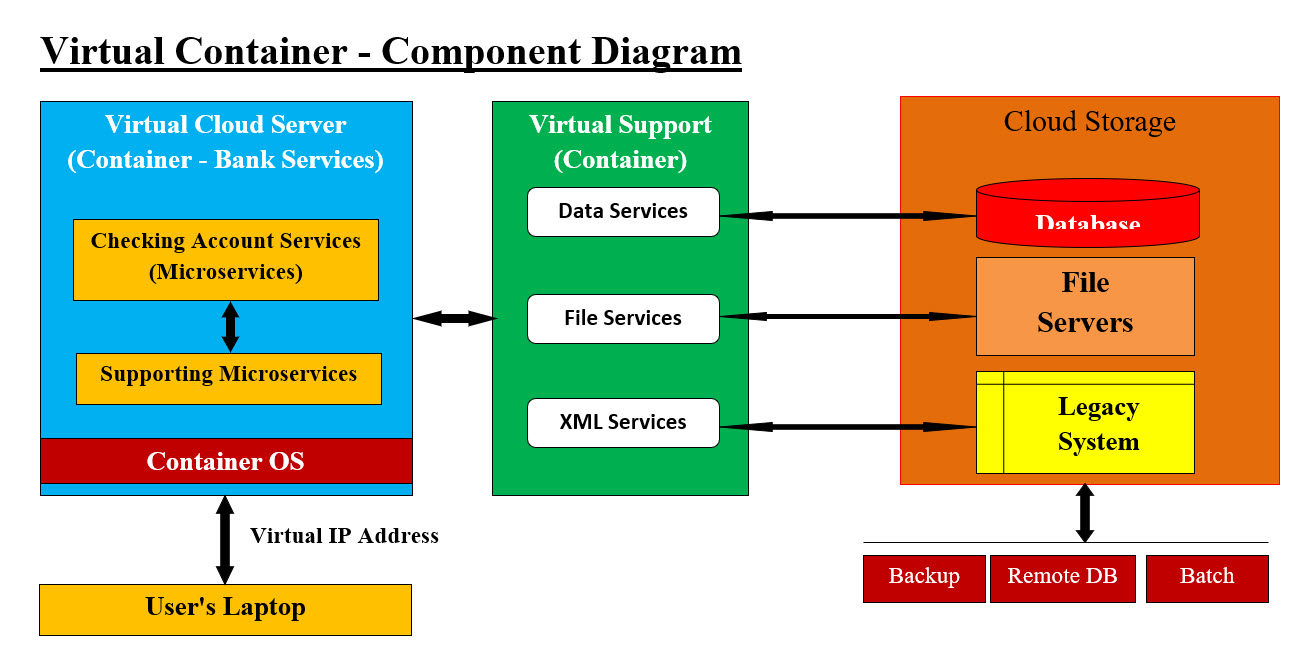
Image #1 Containers-Components: The best way to explain the difference between Component and Container is the example of creating a virtual server (container) where applications (components) as well as virtual data storage(components) are the components running withing the virtual server (container). Therefore, a container would have components run within it. Another example: a Virtual Private Server Hosting (Container) provides a virtualized environment (Component) for the website, which is isolated from other accounts on the same server. Within the virtual environment (which can also be a container) run a number of applications (components). The website can also be structured into Containers and Components. Image #1 presents a rough draft of a Container-Component structure, where there are two virtual severs. The first virtual cloud server (containers) has a bank service application (Microservers) and all its supporting software. The virtual server or Virtual Machine (VM) – a container – has its own Operation system and resources. As for the second virtual cloud server-container has all the supporting data services applications. Containers-Components Structure: It is critical to start thinking in term of container and components in order to structure hosting as services of Containers and Components Hosting cost: Search the internet for average annual hosting cost for small and big businesses, we found the following: How much should you pay for web hosting? Cloud hosting: Conventional web hosting companies charge $30 to $400 per month for cloud hosting. Some companies, like Amazon Web Services, provide modular cloud hosting plans starting as low as $5 per month. Dedicated hosting: Dedicated hosting plans cost anywhere from $50 to $700 per month. How much does an average company spend on AWS? AWS pricing varies based on the size of the organization. For an enterprise with a headcount of 200, the expected cost range is between $907,900 and $1,325,100. Larger enterprises with a headcount of 1,000 can anticipate costs within the range of $2,717,100 and $6,384,300. How much does hosting cost yearly? On average, you can expect to pay anywhere from about $95 to $360 per month for a dedicated hosting plan. Dedicated hosting is ideal for businesses with custom software requirements, high traffic volumes and enhanced security considerations. May 15, 2024. The Harsh Truth: The actual cost of hosting for anyone including big businesses is very hard to calculate due to many important factors. Host can range from $19 per month for shared hosting to more than $6,384,300 as shown in above. There is hidden cost which comes with using the internet. For example, Security, Resources, Services and Support, Cost in term time and money plus the cost of Site Outages and Downtime must also be included. Hosting Issues: Issues with hosting are numerous and we will be focusing on: 1. Security 2. Zero-Trust Architect-Design (ZTAD) Report Card 3. Resources 4. Services and Support 5. Cost in term time and money 6. Site Outages and Downtime Each of the listed issues has its own cost and they must be addressed or added to the annual cost. |
|---|