|
|

|
Case Study - Oil and Gas Refinery©
|
|
|
|
Case Study - Oil and Gas Refinery
Introduction:
Our Case Studies - Oil and Gas Refinery is a part of our Virtual Edge Computing with Machine Learning. Our
main goal is to present our Virtual Edge Computing with Machine Learning System as a replacement
of Edge Computing Boxes-System. We believe Edge Computing Boxes-System is an overkill, an added
layer(s) and an overhead in security, maintenance, performance, cost, ..etc.
Letter to The Department of Defense (DoD) and The US Navy is Our Main Target:
Our Black Box:
Our Black Box is an Edge Computing Boxes-System with built-in small size bare-metal servers. Each
bare-metal server runs independently. Our Black Box is an Edge Computing Boxes-System analysis and
architect is an intelligent Automated Integrated System which would be the seed for something bigger
such as mentoring system which would be placed on facilities, sites, ships, ports, camps, ..etc. Such
system would be the global eyes and ears of commend centers with real-time tracking and control.
The Case at Hand (We Have a Different Animal):
After our researching and analysis of Oil and Gas Refinery, our Oil and Gas Refinery Case Study needs to
take a totally different approach. In short, we do have a major case which would impact the world
economy. According to market research by IBIS World, a leading business intelligence firm, the
total revenues for the oil and gas drilling sector came to approximately $2.1 trillion in 2021. Department
of Homeland Security (DHS) calls the energy sector one of the most powerful engines of the American
economy. The consequences of any destructive attack (cyber or not) on oil and gas resources would have
significant financial losses for the private sector to potential physical and economic impacts on
all the world municipalities. A major attack would trigger gasoline and diesel price spikes, panic
buying, and supply shortages across the world.
Vulnerability of Oil and Gas Infrastructure:
The size of any Oil and Gas Infrastructure can be seen from space. For example, Oil Tankers,
pipelines, Oil Rigs in the middle of ocean, storage facilities and some modern petroleum refineries
process as much as 1.2 million barrels of crude oil per day, cannot be missed. The exhaust
coming out of these refineries can be seen from miles. In short, almost all of Oil and Gas
Infrastructures are vulnerable for assaults, cyber attack, drones attacks, sabotage plus the
consequences can be devastating. On September 14, 2019, two major Saudi Oil Installations were hit
by Drone Strikes and the attacks immediately escalated tensions in the Persian Gulf amid a standoff
between the United States and Iran. The monstrous cyber attack on Saudi Aramco, one of the world's
largest oil companies. The assault was the most alarming in a string of hacking attacks on petrochemical
plants in Saudi Arabia. In a matter of hours, 35,000 computers were partially wiped or totally destroyed.
Our Goal:
Our goal is providing the analysis-architect-design as a security solution for Oil and Gas Refinery
using our Virtual Edge Computing with Machine Learning. Since "We Have a Different Animal" plus the
Vulnerability of the Gas Refinery, our analysis-architect-design would require different approach than
our analysis-architect-design for cloud system, Data Center, Autonomous Vehicles or networks. We need
to see how the military such as the navy and how the US Navy would handle their approach of securing
their troops, tankers, ships, equipments, hardware, ..etc.
How Can These Oil and Gas Infrastructures Be Secured?
What are we dealing with?
Security for Oil and Gas Infrastructure takes on a totally different meaning from what we have
been developing for cloud system, Data Center, Autonomous Vehicles or networks. Oil and Gas
Infrastructure is an open fields of buildings, pipes, trucks, Equipments, supertankers, Oil Rig
middle of ocean, storage facilities, computer system, financial payment system, tracking system, plus
at this point in analysis and architecting we are new to this field and we do not have the entire
picture.
The following is very much what we believe we need to cover:
• Quick Components Analysis
• Strategy
• Redefine Security
• Data (Paperless) Trail, Updates and System Image - Black Box
• Using Our Autonomous Vehicle Approaches and Tools
Quick Components Analysis:
Oil and Gas industries are composed of huge components in size, operations and widely dispersed.
Architecting and developing security systems for the Oil and Gas industries is the biggest challenge
which we ever would imagine. We need to start listing all the possible attacks, their size and
sophistications. Nothing is trivial when it comes to security. We need to identify the threat category,
type, size and the chance of such attack would take place plus the location and the
frequencies of events.
Goals of Quick Components Analysis:
Our approaches when dealing with data is create Business Vocabulary, Dictionary, ID Numbers and
structure of lookup information tables. Such approach keep everyone in the same loop plus the data
can grow without any additional tables of structure.
Business Vocabulary:
Business Vocabulary is critical in communication where information is understood. While many terms
are universal throughout the business world, specific fields of business would have a specific Vocabulary.
Dictionary and ID Numbers:
Technology jargon may require some help from the business dictionary. ID would help with quick
identification and computer processes.
Dictionary:
Technology jargon is a collection of words and phrases that people use in industries dealing with
the daily tasks using their terminology which would help them communicate more quickly and
effectively. For starting any project, it is best practice that we build a Technical Dictionary for
new comers to the business, project and teams.
ID Numbers:
Our view of ID numbers is that these ID numbers can be used for communication, automation, tracking and
computer processing. The following table is our attempt to turn a number of definitions into both
abbreviation and ID numbers. We would be using ASCII values for ID numbers. We used ASCII value of each
letter or char to build the ID number. For example:
AC = 6567
A is ASCII 65, C is ASCII 67
WS = 8783
W is ASCII 87, S is ASCII 83
|
Name
|
Abbrv
|
ID
|
Definition and Comments
|
|
Accidents
|
AC
|
6567
|
There have been many accidents in the oil and gas industry that have caused many fatalities with loss
of assets and/or with a huge impact on the environment. Major causes of an accident can include material,
structural and mechanical failures and malfunction, human and procedural errors associated with poor
training, natural causes, etc.
|
|
Arsenal
|
AR
|
6582
|
What are the 3 types of arson?
The first degree is when the building is burned with knowledge that someone is in the building or at home.
Second degree arson is when an empty building or other structure without persons has been immolated.
The third degree occurs when an area or property has been destroyed by fire with no one else present.
|
|
Asphyxiation- suffocation
|
AP
|
6580
|
Asphyxiation, or suffocation, occurs when the body is deprived of oxygen.
Asphyxia can result from drowning, asthma, choking, strangulation, seizure, drug overdose, or
inhaling chemical substances. Asphyxiation can lead to loss of consciousness, brain injury, and death.
|
|
Assaults
|
AS
|
6583
|
Oil and Gas platforms offer very appealing targets to terrorists and bandits. Not only does terrorist
occupation of an oil platform offer potential for impeding the flow of oil and destroying a valuable
asset, it also has the potential for a massive environmental disaster.
The threat of the destruction of the rig to extort concessions on oil revenues or to receive ransom
for oil workers.
|
|
Availability
|
AV
|
6586
|
Our definition of Availability is building components which perform the following:
• Failure Prevention
• Recovery Decisions
• Redirect
• Saving the State for Recovery
|
|
Blowouts of Pressurized Gas
|
BP
|
6680
|
A blowout is the uncontrolled release of crude oil and/or natural gas from an oil well or gas
well after pressure control systems have failed. Modern wells have blowout preventers (BOP Systems)
intended to prevent such an occurrence.
|
|
Bombs
|
BM
|
6677
|
Oil and gas facilities and equipments can be easy bumped by terrorists.
Terrorism presents a potential threats such as biological, chemical, and explosive.
|
|
Business Loss
|
BL
|
6676
|
Shutdown, Sabotage or any event which affects the oil and gas production would cause business loss or loss of revenues.
|
|
Communication
|
CM
|
6777
|
See the Communication Section for more details.
|
|
Computer System
|
CS
|
6783
|
See the Computer System Section for more details.
|
|
Corrosiveness or Corrosion
|
CR
|
6782
|
Corrosion is the deterioration of a metal or its properties attacks every component at every
stage in the life of every oil and gas field.
|
|
Data Breach
|
DB
|
6866
|
A data breach is a security violation, in which sensitive, protected or confidential data is
copied, transmitted, viewed, stolen or used by an individual unauthorized to do so. Other terms
are unintentional information disclosure, data leak, information leakage and data spill.
|
|
Drone Attacks
|
DA
|
6865
|
A drone is an unmanned aircraft. Drones are more formally known as unmanned aerial vehicles or unmanned aircraft systems.
|
|
Explosions
|
EX
|
6988
|
Oil and gas facilities have the potential of explosions.
|
|
Facilities
|
FC
|
7067
|
See the Facilities section for more details.
|
|
Failure
|
FA
|
7065
|
Communication technologies had enabled oil and gas operations to become more efficient and allowing
environmental, safety and health risks to be managed more effectively. But since oil and gas
facilities are routinely located in undersea and remote locations, new infrastructure challenges
appear regularly on the horizon and Failure is an issue.
|
|
Fire
|
FR
|
7082
|
Fire and explosions after the release of hydrocarbons which is a mixture of gases or liquid drops
dispersed in a cloud together with air can be ignited.
|
|
Flooding
|
FL
|
7076
|
Extreme temperatures, winds, hurricanes, droughts, flash flooding, storm surges, and forest fires are
expecting to increase globally, with potentially severe off-site consequences through toxic-release,
oil spillages, fire, or explosion and the safety of people and the environment.
|
|
Hacking Internal
|
HI
|
7273
|
An internal attack occurs when an individual or a group within an organization seeks to
disrupt operations or exploit organizational assets.
|
|
Hacking External
|
HE
|
7269
|
External hacks typically look for information they can sell or use to make a profit, so
if a hacker penetrates your network or software, then hides valuable information and
demands a ransom of money in return for releasing the information back to you, then external
hacks could be monetarily more harmful.
|
|
Hazardous Objects
|
HO
|
7279
|
See the Hazardous Objects section for more details
|
|
Hazardous Materials
|
HM
|
7277 |
Oil and gas hazardous material means any waste, pollutant, hazardous substance, toxic
substance, hazardous waste, special waste, industrial substance or waste, petroleum or
petroleum-derived substance or waste.
|
|
Interference
|
IF
|
7370
|
Interference is anything that blocks or changes the source's intended meaning of the message.
This can be external or internal.
|
|
Interruption of Service
|
IT
|
7384
|
Interruption in service means a detectable interruption or degradation in service without any further
requirement that such interruption or degradation render companies or teams incapable of supporting
their normal business function.
|
|
Latency
|
LT
|
7684
|
Network latency is an expression of how much time it takes for a packet of data to get from one
designated point to another.
|
|
Operations
|
OP
|
7980
|
See Operations section for more details.
|
|
Outdated Equipments
|
OE
|
7969
|
Obsolete Equipment means any machinery, equipment, furniture, apparatus, tools or implements or
other similar property that may be defective or may have become worn out or obsolete or no longer
used or useful in the operations of the Borrower or its Subsidiaries
|
|
Outages
|
OT
|
7084
|
In general, there are four main types of power outages: blackouts, brownouts, permanent faults,
and rolling blackouts.
|
|
Payment System Damage
|
PD
|
8068
|
The interruption of payment to contractors and consultants due to the software system failure to perform.
|
|
Piracy
|
PI
|
8073
|
Piracy is an act of robbery or criminal violence by ship or boat attackers upon another
ship or a coastal area, typically with the goal of stealing cargo and other valuable goods. Those
who conduct acts of piracy are called pirates, vessels used for piracy are pirate ships.
|
|
Plant Shutdown
|
PS
|
8083
|
A shutdown is simply a disruption in the refining process. A turnaround is a planned break in
production so that maintenance may be performed. The effects of a shutdown or a turnaround can
make a difference in the supply available to retail fuel outlets. These turnarounds can be due
to maintenance, renovating, or refitting facilities.
|
|
Production Loss
|
PL
|
8076
|
It could be due to equipment failure, breakdown, stoppage, shutdown, planned maintenance, operation loss
or loss of power.
|
|
Reliability
|
RL
|
8376
|
Reliability in communication networks in the best of situations means that calls and messages are
guaranteed to reach their destination complete, secure, and in the order they were sent.
|
|
Sabotage
|
SB
|
8366
|
To damage or destroy equipment, weapons, buildings, productions, operations or systems.
|
|
Sabotage Infrastructure
|
SI
|
8373
|
Sabotage Infrastructure means an unauthorized with the intended to cause and having the means to cause
damage, plus substantial and widespread interruption or impairment of a fundamental service rendered
by the critical infrastructure.
|
|
Shipping and Ports
|
SP
|
8380
|
See the Shipping and Ports section for more details.
|
|
System Wipe Out
|
SW
|
8387
|
Completely wiping out of the entire computer system
|
|
Terrorists Attacks
|
TA
|
8465
|
Attacks on oil and gas installations have become the weapon of choice for international terrorism attacks.
|
|
Theft
|
TF
|
8470
|
The impact of oil theft in terms of domestic resource utilization, revenue loss, transnational
economic impact, regional insecurity, community impact is a big concern.
|
|
Toxicity
|
TO
|
8479
|
the quality, state, or relative degree of being poisonous
|
|
Vandalism
|
VD
|
8668
|
Crude oil pipeline vandalism can lead to 6% or 10% decrease in oil revenue generated.
|
|
Weather and Storms
|
WS
|
8783
|
Unfavorable climate can act as a barrier to communication leading to wrong perceptions or decision.
|
Computer System - ID = CS 6783:
Today computer systems have become an essential part of everyday life, and having major impact on our modern society.
Both hardware and software work together to run the computer system. Cybersecurity is critical to any cloud
systems. Therefore, computer system security is essential to run any business or governments.
Each ID would be used in the analysis and architecting to identify the threat-type. For example, Oil
and gas Control Center would have:
Vulnerability Type + %Probability = 01CH_99 (Computer Hacking - Malicious Code - 99% change of occurring)
The following table identifies and categorizes the type of attack on any computer system.
|
ID
|
Threat Name-Type
|
Definition and Comments
|
|
7269
|
Hacking External - HE
|
Hacking - All types of system hacking such as malicious code, spyware, Ransomware, viruses, worms, cross-site
scripting, IP Spoofing, Eavesdropping, Phishing/Social Engineering Attacks, ...etc.
|
|
7273
|
Hacking Internal - HI
|
An internal attack occurs when an individual or a group within an organization seeks to
disrupt operations or exploit organizational assets.
|
|
6866
|
Data Breach - DB
|
A data breach is a security violation, in which sensitive, protected or confidential data is
copied, transmitted, viewed, stolen or used by an individual unauthorized to do so. Other terms
are unintentional information disclosure, data leak, information leakage and data spill.
|
|
8387
|
System Wipe Out - SW
|
Completely wiping out of the entire computer system
|
|
8373
|
Sabotage Infrastructure - SI
|
Sabotage Infrastructure means an unauthorized with the intended to cause and having the means to cause
damage, plus substantial and widespread interruption or impairment of a fundamental service rendered
by the critical infrastructure.
|
Operations - ID = OP 7980:
Oil and gas operations are the processes that energy companies use every day to run their
businesses. These include systems involved in well productivity, financial and operating
performance measurement, asset management, health and safety management, and many others.
|
ID
|
Threat Name-Type
|
Definition and Comments
|
|
8083
|
Plant Shutdown - PS
|
A shutdown is simply a disruption in the refining process. A turnaround is a planned break in
production so that maintenance may be performed. The effects of a shutdown or a turnaround can
make a difference in the supply available to retail fuel outlets. These turnarounds can be due
to maintenance, renovating, or refitting facilities.
The cost associated with Shutdown and turnaround are substantial plus labor intensive.
|
|
8366
|
Sabotage - SB
|
To damage or destroy equipment, weapons, buildings, productions, operations or systems.
|
|
6676
|
Business Loss - BL
|
Shutdown, Sabotage or any event which affects the oil and gas production would cause business loss or loss of revenues.
|
|
7084
|
Outages - OT
|
In general, there are four main types of power outages: blackouts, brownouts, permanent faults,
and rolling blackouts.
The process is triggered by any degradation or interruption of a product or service, and is
considered resolved when the product or service is restored to normal operations.
|
|
8076
|
Production Loss -PL
|
It could be due to equipment failure, breakdown, stoppage, shutdown, planned maintenance, operation loss
or loss of power.
|
|
8068
|
Damage Payment Systems - PD
|
The interruption of payment to contractors and consultants due to the software system failure to perform.
|
Facilities - ID = FC 7067:
Oil and gas facility means equipment or improvements used or installed at an oil and gas location
for the exploration, production, withdrawal, gathering, treatment, or processing of oil or natural gas.
|
1. Oil and Natural Gas – Well Site
|
2. Central Tank Battery
|
3. Produced Water Injection Facility
|
|
4. Gathering Compressor Station
|
5. Treatment Without Compression
|
6. Plant – NGL Extraction
|
|
7. Fractionation
|
8. Transmission Compressor Station
|
9. Underground Storage Facility
|
|
10. Pipeline Breakout Facility
|
11. Truck Station
|
12. Tank Farm
|
|
13. Oil and Natural Gas Refined Petroleum
|
14. Pipeline Pump Station
|
15. Oil Refinery
|
|
16. Refined Petroleum
|
17. Product Terminal
|
18. Fire-Fighting Equipment
|
|
ID
|
Threat Name-Type
|
Definition and Comments
|
|
8470
|
Theft - TF
|
The impact of oil theft in terms of domestic resource utilization, revenue loss, transnational
economic impact, regional insecurity, community impact is a big concern. Global oil theft is
estimated at $133 billion and this equates to about 5% to 7% of all crude oil and refined
fuels produced.
Oil theft regularly occurs across the supply chain, from the wellhead, gathering
station, crude oil pipeline, oil storage facility, and oil bunkering station, during crude oil
tanker loading, during illegal ship-to-ship transfers facilitated by oil tanker crews, and owing
to violent acts of robbery and piracy at sea. Some of the crude oil stolen is refined into
primitive fuels.
|
|
7082
|
Fire - FR
|
The top causes of fatalities in the oil and gas industry are similar to those found in
general industry. However, the fatality rate for oil and gas workers is seven times higher
than other industries, according to the CDC. Recognizing the top hazards causing fatalities
and injuries is the first step in developing plans, procedures and training that prevent
these incidents.
Fire and explosions after the release of hydrocarbons which is a mixture of gases or liquid
drops dispersed in a cloud together with air can be ignited. Oil release on the subsea and
on sea surfaces. There have been many accidents in the oil and gas industry that have caused
many fatalities with loss of assets and/or with a huge impact on the environment. Major
causes of an accident can include material, structural and mechanical failures and
malfunction, human and procedural errors associated with poor training, natural causes, etc.
|
|
8668
|
Vandalisms - VD
|
Crude oil pipeline vandalism can lead to 6% or 10% decrease in oil revenue generated. Pipeline
vandalism is the willful or deliberate act of damaging petroleum pipelines with the sole aim of
stealing crude oil and associated petroleum products.
|
|
8366
|
Sabotage - SB
|
The sabotage of two gas pipelines between Russia and Europe should serve as a wake-up
call to the continent to protect its critical infrastructure.
|
|
7076
|
Flooding - FL
|
There has been much discussion regarding the increasing frequency and intensity of storms around the world.
Climate change is anticipated to contribute to the faster aging and degradation of the oil infrastructure
processes, from the oil extraction and upstream to the storage, refining and distribution processes, reducing
lifecycle, service level, and leading to major disasters.
Extreme temperatures, winds, hurricanes, droughts, flash flooding, storm surges, and forest fires are
expecting to increase globally, with potentially severe off-site consequences through toxic-release,
oil spillages, fire, or explosion and the safety of people and the environment.
|
Communication - ID = CM 6777:
What are the types of communication exist today and how applicable to the Oil and Gas industries?
The goal of this section is to secure Oil and Gas Communication and provide security solutions to existing communication issues.
Types of Communication Exist Today:
|
1.
|
Satellite Communication:
Satellite communication, in telecommunications, the use of artificial satellites to provide
communication links between various points on Earth.
|
|
2.
|
Mobile:
Wireless communication is the transfer of information between two or more points without the use of
an electrical conductor, optical fiber or other continuous guided medium for the transfer. The most
common wireless technologies use radio waves.
Mobile communication describes the use of various technological systems in order to communicate while
one is away from a fixed location.
|
|
3.
|
Cloud:
Cloud communications are Internet-based voice and data communications where telecommunications
applications, switching and storage are hosted by a third-party outside of the organization using
them, and they are accessed over the public Internet.
|
|
4.
|
Microwave Communication:
The transmission of signals by sending microwaves, either directly or via a satellite. The receivers
for microwave signals are usually disc-shaped antennae from a foot to a few feet across and are often
seen installed in business locations or near private homes.
|
|
5.
|
Radio:
Radio is the transmission of signals by modulation of electromagnetic waves with frequencies below
those of visible light. Electromagnetic radiation travels by means of oscillating electromagnetic
fields that pass through the air and the vacuum of space. Information is carried by systematically
changing (modulating) some property of the radiated waves such as amplitude, frequency, or phase.
|
|
6.
|
Infrared Communication:
IR, or infrared, communication is a common, inexpensive, and easy to use wireless communication
technology. IR light is very similar to visible light, except that it has a slightly longer
wavelength. This means IR is undetectable to the human eye - perfect for wireless communication.
|
|
7.
|
Wi-Fi:
Abbreviation for wireless fidelity: a system used for connecting computers and other electronic
equipment to the internet without using wires: Built-in Wi-Fi now comes as a standard feature.
Wi-Fi is a wireless technology used to connect computers, tablets, smart phones and other devices
to the internet. Wi-Fi is the radio signal sent from a wireless router to a nearby device, which
translates the signal into data you can see and use.
|
|
8.
|
Bluetooth Technology:
Bluetooth technology allows devices to communicate with each other without cables or wires. Bluetooth
relies on short-range radio frequency, and any device that incorporates the technology can communicate
as long as it is within the required distance.
|
How can we secure these communication media and their equipments?
|
ID
|
Threat Name-Type
|
Definition and Comments
|
7269
7273
|
Hacking External - HE
Hacking Internal - HI
|
Hacking - All types of system hacking such as malicious code, spyware, Ransomware, viruses,
worms, cross-site scripting, IP Spoofing, Eavesdropping, Phishing/Social Engineering Attacks, ... etc.
An internal attack occurs when an individual or a group within an organization seeks to
disrupt operations or exploit organizational assets.
|
|
8668
|
Vandalism - VD
|
Vandalism is intentional destruction or damage to property.
Electronic vandalism is the act of stealing or deliberately damaging any computer hardware
or software or the unauthorized use of, or entry into, any computer program or system not
intended for authorized use is prohibited.
|
|
8783
|
Weather and Storms - WS
|
Unfavorable climate can act as a barrier to communication leading to wrong perceptions or decision.
Noise: Noise is a physical barrier to effective communication. Noise may have its
origin from an external source or may exist even in the communication loop.
Bad weather can affect communications networks in a range of different ways. At the
simplest end of the spectrum, from a basic clarity and audibility perspective, high
winds and stormy weather can impact voice communication, making it far more difficult
for radio users to hear each other.
Satellite signals are disturbed by atmospheric effects on the path between the satellite and
the receiver antenna. These effects are mostly rain, cloud and gaseous attenuation.
|
|
7065
|
Failure - FA
|
Communication technologies had enabled oil and gas operations to become more efficient and allowing
environmental, safety and health risks to be managed more effectively. But since oil and gas
facilities are routinely located in undersea and remote locations, new infrastructure challenges
appear regularly on the horizon and Failure is an issue.
|
|
7370
|
Interference - IF
|
Interference is anything that blocks or changes the source's intended meaning of the message.
This can be external or internal.
|
|
7384
|
Interruption of Service - IT
|
Interruption in service means a detectable interruption or degradation in service without any further
requirement that such interruption or degradation render companies or teams incapable of supporting
their normal business function.
|
|
8366
|
Sabotage - SB
|
To damage or destroy equipment, weapons, buildings, productions, operations or systems.
|
|
8376
|
Reliability - RL
|
Reliability in communication networks in the best of situations means that calls and messages are
guaranteed to reach their destination complete, secure, and in the order they were sent.
Here are a few important ways to help improve reliability:
• Improve the reliability of individual components of the network
• Increase the number of alternative paths available
• Improve the experience of disruption mitigation
|
|
6586
|
Availability - AV
|
Our definition of Availability is building components which perform the following:
• Failure Prevention
• Recovery Decisions
• Redirect
• Saving the State for Recovery
|
|
7684
|
Latency - LT
|
What is Latency?
Can Communication Latency become an issue?
Network latency is an expression of how much time it takes for a packet of data to get from one
designated point to another. The Internet is a very large wide-area network (WAN). Distances in
the transmission medium, the number of hops over equipment, servers, the traffic on these servers
add to latency measurement. For mobile you need to add mobile towers and satellites communication.
Cloud and Latency:
Intelligent Latency Driver:
An architect needs to address Latency in the architect-design and keep statistics of peak time
and routes used. We need to build a Latency testing driver which is an intelligent software that
would run and track routes, errors, issues and times. It would also gives the best routes/time and
possible issues with the system. Such driver would be running and mapping the system end-to-end. It
could be a part of the Logging services.
|
|
7969
|
Outdated Equipments - OE
|
Lack Of Competitive Edge
Equipment Failure
Security Breaches
Performance
Higher maintenance and repair costs
|
Terrorists Attacks - ID = TA 8465:
Attacks on oil and gas installations have become the weapon of choice for international terrorism attacks.
Every sector of the oil and gas fuel cycle is quite vulnerable to verities of terrorist threats. Regardless
of intelligence services, or military forces, nothing have been able to prevent terror attacks from
happening. A number of terror attacks on oil and gas installations have been performed by well trained-and well
equipped armed forces. The following are some of reported Terrorist Attack on:
• Development and Exploration Sites
• During Maritime Transport
• Distribution System
• Refineries
• Suicide Terrorist Attack of an Offshore Platform
|
ID
|
Threat Name-Type
|
Definition and Comments
|
|
6865
|
Drone Attacks - DA
|
A drone is an unmanned aircraft. Drones are more formally known as unmanned aerial vehicles or unmanned aircraft systems.
Drones now have many functions, ranging from monitoring climate change to carrying out search operations
after natural disasters, photography, filming, and delivering goods. But their most well-known and
controversial use is by the military for reconnaissance, surveillance and targeted attacks.
Drone attacks can be conducted by commercial dropping bombs, firing a missile, or crashing into a target.
Drone attacks on two key oil installations inside Saudi Arabia on Saturday, damaging facilities that
process the vast majority of the country’s crude output and raising the risk of a disruption in world
oil supplies.
|
|
6583
|
Assaults - AS
|
Oil platforms offer very appealing targets to terrorists and bandits. Not only does terrorist
occupation of an oil platform offer potential for impeding the flow of oil and destroying a valuable
asset, it also has the potential for a massive environmental disaster.
The threat of the destruction of the rig to extort concessions on oil revenues or to receive ransom for oil workers.
|
|
6677
|
Bombs - BM
|
Oil and gas facilities and equipments can be easy bumped by terrorists.
Terrorism presents a potential threats such as biological, chemical, and explosive.
|
|
6582
|
Arsenal - AR
|
What are the 3 types of arson?
The first degree is when the building is burned with knowledge that someone is in the building or at home.
Second degree arson is when an empty building or other structure without persons has been immolated.
The third degree occurs when an area or property has been destroyed by fire with no one else present.
|
|
6988
|
Explosions - EX
|
Oil and gas facilities have the potential of explosions.
|
Shipping and Ports - ID = SP 8380:
Oil is the largest commodity moved by water, which is the most efficient and cost effective form
of transportation. Tankers travel along fixed maritime routes called chokepoints. These chokepoints
are strategic arteries for energy transport and therefore at high risk for piracy, terror attacks
and hazardous oil spills. Most LNG is transported by tankers called LNG carriers in large, onboard,
super-cooled (cryogenic) tanks.
Big, slow moving crude oil tankers are relatively easy targets with thin crews. Usually pirates are
looking to extract a ransom, but not always. In October 2002 for instance, maritime terrorists bombed
French oil tanker MV Limburg off the coast of Yemen. While the two latest ships seized in the Indian
Ocean this month were carrying crude oil not refined fuels, the bulk of smaller oil product tankers
pass through pirate waters on their way through the Suez Canal. Terror organizations have planned
several attacks against oil tankers in the Arabian Gulf and Horn of Africa. According to FBI Director
Robert Mueller, "There have been any number of attacks on ships that have been thwarted."
Increasingly, the maritime domain and energy sector has turned to technology to improve production,
cost and reduce delivery schedules. As crews get smaller and ships get bigger, they increasingly rely
on automation and remote monitoring, meaning key components, including navigational systems, which can be
hacked. Plus equipment to oil and gas monitors are connected to the internet using serial ports with poor security.
Hackers recently shut down a floating oil rig by tilting it, while another rig was so riddled with computer
malware that it took 19 days to make it seaworthy again; Somali pirates help choose their targets by viewing
navigational data online, prompting ships to either turn off their navigational devices, or fake the data so
it looks like they’re somewhere else. Hackers infiltrated computers connected to the Belgian port of Antwerp,
located specific containers, made off with their smuggled drugs and deleted the records.
|
ID
|
Threat Name-Type
|
Definition and Comments
|
|
8465
|
Terrorists Attacks - TA
|
Big, slow moving crude oil tankers with thin crews are easy
target for Terrorists Attacks. The same thing can be said about ports.
|
|
8073
|
Piracy - PI
|
Pirates use the internet to track and hack ships navigation system plus they would be able
to view navigational data online. They use the internet to misguide ships to either turn
off their navigational devices, or fake the data so it looks like they are somewhere else.
|
|
6567
|
Accidents - AC
|
Tanker or ships accidents have serious consequences. They are large ships that require skill to
operate and navigate. Accidents can happen for any number of reasons, but often negligence
plays a role. The most common types of accidents with these large vessels include running aground
or into reefs in shallow waters, colliding with other vessels or structures like bridges, and fires
or explosions aboard the ship. These kinds of accidents most often occur close to shore, sometimes
right in port while loading or unloading cargo.
|
7269
7273
|
Hacking External - HE
Hacking Internal - HI
|
Any computer system could be hacked if not protected against hacking.
|
|
8366
|
Sabotage - SB
|
To damage or destroy equipment, weapons, buildings, productions, operations or systems.
|
Hazardous Objects - ID = HO 7279:
Safety Hazards Associated with Oil and Gas Extraction Activities Oil and gas well drilling
and servicing activities involve many different types of equipment and materials. Recognizing
and controlling hazards is critical to preventing injuries and deaths.
1. Chemical Hazards
2. Gas Hazards
3. Hazardous Materials
4. Accident involving vehicle and equipments
5. Personal injuries
6. Explosions
7. Fires
8. Falling off
9. Confined Spaces
10. Hazards work
11. High Pressure Lines
12. High Pressure Equipment
13. Electrical Hazardous
14. Energy Hazardous
15. Machine Hazards
16. Heat
17. Exhaustions
18. Blowouts of Pressurized Gas
|
ID
|
Threat Name-Type
|
Definition and Comments
|
|
8479
|
Toxicity - TO
|
What is oil toxicity?
Oil, in high enough concentrations, can poison animals by internal and external routes of
exposure. Birds and mammals often die because oil fouls fur and feathers so that they no longer
insulate. Smaller organisms can be smothered by a thick layer of oil washing ashore.
What causes oil toxicity?
All crude oil contains VOCs, which readily evaporate into the air, giving crude oil a distinctive
odor. Some VOCs are acutely toxic when inhaled, in addition to being potentially cancer-causing.
|
|
7082
|
Fire - FR
|
The top causes of fatalities in the oil and gas industry are similar to those found in general
industry. However, the fatality rate for oil and gas workers is seven times higher than other
industries, according to the CDC. Recognizing the top hazards causing fatalities and injuries is
the first step in developing plans, procedures and training that prevent these incidents.
Fire and explosions after the release of hydrocarbons which is a mixture of gases or liquid drops
dispersed in a cloud together with air can be ignited. Oil release on the subsea and on sea
surfaces. There have been many accidents in the oil and gas industry that have caused many fatalities
with loss of assets and/or with a huge impact on the environment. Major causes of an accident can
include material, structural and mechanical failures and malfunction, human and procedural errors
associated with poor training, natural causes, etc.
|
|
6782
|
Corrosiveness or Corrosion - CR
|
Corrosion is the deterioration of a metal or its properties attacks every component at every
stage in the life of every oil and gas field. From casing strings to production platforms, from
drilling through to abandonment, corrosion is an adversary worthy of all the high technology
and research we can throw at it. Oilfield equipment corrosion occurs under the influence of
mineral salts and corrosive aggressive gases such as hydrogen sulfide, carbon dioxide, hydrogen
chloride and oxygen, which are dissolved in the formation and bottom water.
|
|
6580
|
Asphyxiation- suffocation - AP
|
Asphyxiation, or suffocation, occurs when the body is deprived of oxygen. Asphyxia can
result from drowning, asthma, choking, strangulation, seizure, drug overdose, or inhaling
chemical substances. Asphyxiation can lead to loss of consciousness, brain injury, and death.
|
|
7277
|
Hazardous Materials - HM
|
Oil and gas hazardous material means any waste, pollutant, hazardous substance, toxic
substance, hazardous waste, special waste, industrial substance or waste, petroleum or
petroleum-derived substance or waste.
|
|
6680
|
Blowouts of Pressurized Gas - BP
|
A blowout is the uncontrolled release of crude oil and/or natural gas from an oil well or gas
well after pressure control systems have failed. Modern wells have blowout preventers (BOP Systems)
intended to prevent such an occurrence.
Oil rig blowouts can occur when the rig applies too much pressure during the drilling, causing the
pool of underground oil to erupt.
The two main causes of a subsea blowout are equipment failures and imbalances with encountered
subsurface reservoir pressure.
|
Vulnerability Types - ID:
Our analysis needs to figure out which category has higher chance of taking place where we would
be able to start design-architect our security system. Looking at Table #1, we can set the
ranking of vulnerability as follows:
1. Hazardous Objects - ID = HO 7279
2. Terrorists Attacks - ID = TA 8465
3. Facilities - ID = FC 7067
4. Operations - ID = OP 7980
5. Computer System - ID = CS 6783
6. Communication - ID = CM 6777
7. Shipping and Ports - ID = SP 8380
|
No
|
Component Name
|
Vulnerability Types -ID
|
Definition and Comments
|
|
1
|
Upstream Pipelines
|
Hazardous Objects-7279
Terrorists Attacks-8465
Facilities-7067
Operations-7980
|
Upstream for oil and gas production is about extracting oil and natural gas from the ground.
Upstream works include the exploration and production of crude oil and natural gas.
Upstream oil and gas production means that companies who identify, extract, or produce
raw materials, would pass their products through pipelines to refinery.
|
|
2
|
Downstream Pipelines
|
Hazardous Objects-7279
Terrorists Attacks-8465
Facilities-7067
Operations-7980
|
Downstream operations are oil and gas processes is bring usable products to end-users and consumers.
It is the final step in the production process.
Downstream oil and gas production engages in anything related to the post-production of crude oil and natural gas activities.
|
|
3
|
Midstream Pipelines
|
Hazardous Objects-7279
Terrorists Attacks-8465
Facilities-7067
Operations-7980
|
Midstream refers to points in the oil production process that falls between upstream and
downstream. In particular, midstream activities include the storage, processing, and
transportation of petroleum products. These may include companies that specialize in operating
tanker ships, pipelines, or storage facilities.
The midstream sector covers transportation, storage, and trading of crude oil, natural gas, and refined products.
|
|
4
|
FPS
|
Hazardous Objects-7279
Terrorists Attacks-8465
Facilities-7067
Operations-7980
Shipping and Ports-8380
Computer System-6783
Communication-6777
|
Floating production systems (FPS):
FPS is an umbrella term for all types of floating production systems, including boats, ships and platforms.
|
|
5
|
Block Valves
|
Hazardous Objects-7279
Terrorists Attacks-8465
Facilities-7067
Operations-7980
|
Block valves permit fluids to pass through with minimum flow restriction and pressure loss when
fully open and yet provide a tight seal when fully closed.
Mainline block valves are installed to isolate sections of a pipeline for safety reasons and
maintenance and repair. In the event of a pipeline rupture, the damaged pipeline section may
be isolated by closing off the mainline valves on either side of the rupture location.
|
|
6
|
Control Center
|
Computer System-6783
Communication-6777
Operations-7980
Facilities-7067
Terrorists Attacks-8465
|
Control Room or Control Center is where operators control the production, it is usually
located offshore. The control Center operators control the oil and gas production. It operators
by monitoring the operation to ensure that everything is working properly.
|
|
7
|
Compressor Station
|
Hazardous Objects-7279
Terrorists Attacks-8465
Facilities-7067
Operations-7980
Computer System-6783
|
Compressor stations as the Pump stations for oil are large industrial facilities which maintain
the flow and pressure of natural gas by receiving gas from the pipeline, re-pressurizing it, and
sending it back into the pipeline system.
|
|
8
|
Drilling Ring
|
Hazardous Objects-7279
Terrorists Attacks-8465
Facilities-7067
Operations-7980
Shipping and Ports-8380
Computer System-6783
Communication-6777
|
What is Drilling Ring?
A drilling rig is an integrated system which drills holes or wells into the earth's subsurface, such as oil or water wells, or
holes for piling and other construction purposes.
Types of Drilling Rigs:
1. Land Rigs
2. Submersible Rigs
3. Jack-up Rigs
4. Platform Rigs
5. Semi-submersible Rigs
6. Drill Ship Rigs
|
|
9
|
Headquarters
|
Computer System-6783
Communication-6777
Operations-7980
Facilities-7067
Terrorists Attacks-8465
|
A corporate headquarters is a place where a company's executive management and key managerial
and support staff are located. A corporate headquarters is considered a business's most important
location and may also lend prestige to its host city and help attract other businesses to the area.
|
|
10
|
Gas Fields
|
Hazardous Objects-7279
Terrorists Attacks-8465
Facilities-7067
Operations-7980
Computer System-6783
|
A gas field is an area of natural gas underground, produced by decay of organic material.
A gas field is a deposit that is rich in gas which is an area with lots of gas that we can extract.
|
|
11
|
Gas Processing
|
Hazardous Objects-7279
Terrorists Attacks-8465
Facilities-7067
Operations-7980
Computer System-6783
|
Natural gas processing consists of separating all of the various hydrocarbons and fluids from the
pure natural gas, to produce what is known as 'pipeline quality' dry natural gas.
|
|
12
|
Gas Storage
|
Hazardous Objects-7279
Terrorists Attacks-8465
Facilities-7067
Operations-7980
Computer System-6783
|
Gas storage is principally used to meet load variations. Gas is injected into storage during
periods of low demand and withdrawn from storage during periods of peak demand.
It is also used for a variety of secondary purposes, including balancing the flow in pipeline systems.
|
|
13
|
Fracking
|
Hazardous Objects-7279
Terrorists Attacks-8465
Facilities-7067
Operations-7980
Computer System-6783
|
The process of injecting liquid at high pressure into subterranean rocks, boreholes, etc. It would
force open existing cracks and extract oil or gas.
Hydraulic fracturing, or fracking, is a technique for recovering gas and oil from shale rock. It
involves drilling into the earth and directing a high-pressure mixture of water, sand and chemicals
at a rock layer, to release the gas inside.
|
|
14
|
FPSO
|
Hazardous Objects-7279
Terrorists Attacks-8465
Facilities-7067
Operations-7980
Shipping and Ports-8380
Computer System-6783
Communication-6777
|
Floating Production Storage and Offloading (FPSO)
An FPSO is a floating production system which receives fluids. Such fluild may contain crude oil, water and a host of
other things from a subsea reservoir through risers. It would separate fluids into crude
oil, natural gas, water and impurities within the topsides production facilities onboard.
|
|
15
|
LNG Tankers
|
Hazardous Objects-7279
Terrorists Attacks-8465
Facilities-7067
Operations-7980
Shipping and Ports-8380
Computer System-6783
Communication-6777
|
Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG) Tankercarrier is a ship that is designed for the transport of liquefied natural gas
in its chilled tanks. Compared to conventional vessels, LNG carriers release less greenhouse
gas emissions because of their natural gas-fueled propulsion system.
|
|
16
|
LNG Terminal
|
Hazardous Objects-7279
Terrorists Attacks-8465
Facilities-7067
Operations-7980
Shipping and Ports-8380
Computer System-6783
Communication-6777
|
Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG) Terminal:
LNG terminal includes all natural gas facilities located onshore or in State waters that
are used to receive, unload, load, store, transport, gasify, liquefy or process natural gas.
|
|
17
|
Production Facilities Onboard
|
Hazardous Objects-7279
Terrorists Attacks-8465
Facilities-7067
Operations-7980
Shipping and Ports-8380
Computer System-6783
Communication-6777
|
Oil and gas production facilities must separate, treat, and store (or ship) everything that came out of the well(s).
Oil and gas onboard and offboard production facilities
Onboard Facilities:
Onboard facilities available or situated on a ship, or other vehicle.
Offboard Facilities:
Offboard facilities is not available nor situated on a ship, or other vehicle.
|
|
18
|
Production Platform
|
Hazardous Objects-7279
Terrorists Attacks-8465
Facilities-7067
Operations-7980
Shipping and Ports-8380
Computer System-6783
Communication-6777
|
An oil platform, oil rig, offshore platform, or oil and/or gas production platform is a large
structure with facilities to extract, and process petroleum and natural gas that lie in rock
formations beneath the seabed.
|
|
19
|
Oil Terminals
|
Hazardous Objects-7279
Terrorists Attacks-8465
Facilities-7067
Operations-7980
Shipping and Ports-8380
Computer System-6783
Communication-6777
|
A terminal is an industrial facility used to store oil and/or petrochemical products. Terminals
are made up of underground storage tanks, aboveground storage tanks, or both, and pipelines, which
are used to receive product, as well as transport product to the end user or further storage facilities.
|
|
20
|
Oil Tankers
|
Hazardous Objects-7279
Terrorists Attacks-8465
Facilities-7067
Operations-7980
Shipping and Ports-8380
Computer System-6783
Communication-6777
|
An Oil Tanker is a ship that carries a large amount of oil.
|
|
21
|
Oil Sands
|
Hazardous Objects-7279
Terrorists Attacks-8465
Facilities-7067
Operations-7980
|
Oil sands (or “tar sands” or “bituminous sands”) refer to a mixture of sand, water, clay,
and bitumen (which we have seen refers to the heaviest of hydrocarbon mixtures found in crude
petroleum). The mixture is usually between 1% and 20% bitumen.
|
|
22
|
Ports
|
Hazardous Objects-7279
Terrorists Attacks-8465
Facilities-7067
Operations-7980
Shipping and Ports-8380
Computer System-6783
Communication-6777
|
An oil port is a port that can accommodate giant oil tankers. It is a deepwater harbor that
can receive, load, offload, and store oil. The storage for crude petroleum in oil ports is
usually temporary.
|
|
23
|
Processing
|
Hazardous Objects-7279
Terrorists Attacks-8465
Facilities-7067
Operations-7980
|
The purpose of oil and gas processing is to separate, remove, or transform these various
components to make the hydrocarbons ready for sale. For the hydrocarbons(gas or liquid) to be
sold, they must be: Separated from the water and solids.
|
|
24
|
Pump Station
|
Hazardous Objects-7279
Terrorists Attacks-8465
Facilities-7067
Operations-7980
|
What is a water, oil or gas pump station?
Pump stations are large industrial facilities that maintain the flow and the pressure of whatever is running through the pipes.
For oil, the pump receives oil from the pipeline, re-pressurizing it, and sending it back into the pipeline system.
As for gas it known as Compressor stations which do the same thing for natural gas.
|
|
25
|
Retails
|
Computer System-6783
Communication-6777
Operations-7980
Facilities-7067
Terrorists Attacks-8465
|
Fuel retailing industry comprises companies that operate by selling automotive fuel or
lubricating oils at the retail stores such as service station, fuel stations and similar others.
|
|
26
|
Refinery
|
Hazardous Objects-7279
Terrorists Attacks-8465
Facilities-7067
Operations-7980
Shipping and Ports-8380
Computer System-6783
Communication-6777
|
An oil refinery is a facility that takes crude oil and distills it into various useful
petroleum products such as gasoline, kerosene, or jet fuel. Refining is classified as a downstream
operation of the oil and gas industry, although many integrated oil companies will operate both
extraction and refining services.
|
|
27
|
Seismic
|
Terrorists Attacks-8465
Facilities-7067
Operations-7980
|
Seismic:
Seismic definition is relating to earthquakes or other vibrations of the earth and its crust.
Usually after a few days of seismic activity the volcanic eruption started.
What is seismic in oil and gas?
Seismic surveys in oil and gas exploration are performed to map geological structures beneath the
earth's surface or beneath the seabed. Reflection seismology is generally used during onshore exploration,
and involves sending seismic waves underground.
What is the purpose of seismic?
Seismic surveys is more of a “CAT scan” of the Earth's subsurface. It uses reflected sound waves to produce Seismic
surveys which would help in locating ground water and oil.
What is seismic testing for oil?
Seismic testing involves blasting the seafloor with high-powered air guns - a powerful horn every few seconds.
The returning echoes is measured with long tubes to map offshore oil and gas reserves.
|
|
28
|
Subsea Production System
|
Hazardous Objects-7279
Terrorists Attacks-8465
Facilities-7067
Operations-7980
|
Subsea production systems are typical wells located on the seabed, shallow or deep water. Generally
termed as Floating production system, where the petroleum is extracted at the seabed and the same
can be tied back to an already existing production platform or an onshore facility.
|
|
29
|
Transport Pipelines
|
Hazardous Objects-7279
Terrorists Attacks-8465
Facilities-7067
Operations-7980
|
Pipelines that collect products from sources, such as wells on land or offshore, or from
shipping, such as tankers for oil or liquefied natural gas (LNG). These systems move the product
to storage, processing such as treatment for gas or refining of petroleum.
|
|
30
|
Trucks
|
Hazardous Objects-7279
Terrorists Attacks-8465
Operations-7980
|
A tank truck, gas truck, fuel truck, or tanker truck (American English) or tanker (British English)
is a motor vehicle designed to carry liquids or gases on roads. The largest such vehicles are similar
to railroad tank cars, which are also designed to carry liquid loads.
|
|
31
|
Surveillance Cameras
|
Terrorists Attacks-8465
Facilities-7067
Operations-7980
Computer System-6783
Communication-6777
|
Needed for remote Surveillance and communication
|
|
32
|
Sensors
|
Terrorists Attacks-8465
Facilities-7067
Operations-7980
Computer System-6783
Communication-6777
|
Needed for remote Surveillance
|
Table #1
Table #1 is our attempt to present the Oil and Gas Refinery Operations and the types of vulnerability associated with each.
Security Views:
We would like to remind our audience that our Case Studies - Oil and Gas Refinery is a different
animal.
Our first question when it comes to security:
What are we securing?
Unlike cloud system, Data Center, Autonomous Vehicles or networks,
where we have categorized the system components into:
1. Logical Units -Data, Signals, Software-applications, OS, virtual servers, virtual components, virtual devices
2. Physical Units - automotive parts, bar-metal servers, sensors, NAS, Hard drives, Cache, Buffers,
As for Oil and Gas Refinery case, we would be adding two additional categories:
1. Logical Units -Data, Signals, Software-applications, OS, virtual servers, virtual components, virtual devices
2. Physical Units - automotive parts, bar-metal servers, sensors, NAS, Hard drives, Cache, Buffers,
3. Human Factor - negligence, human errors, poor performance, poor management, .. etc
4. Mother Nature/Environments - hurricanes, winds, rain, earthquakes, wells blowouts, .. etc
Our analysis-architect-design must handle each category differently. The security approach to each would
be quite different. For example, an oil or gas rig in the middle of the ocean facing 500 mile wind storm
plus rain, the last thing such rig would be worried about is any hackers attack. The worries would be
personals and equipments flying off the rig. Therefore, securing personals and equipments must be addressed
and handled to provide security and safety.
Logical Units:
Logical Units would include all the system software, applications, security software, Machine Learning
software, data files and all cloud communication software, which would be in the thousands. Each of these
logical units must be known plus its functionality. Since all Logical Units processes must be tested,
timed (how long it would take to perform its tasks) and stored and ready to be loaded into Cache for execution.
See our Case Study - Autonomous Vehicles© and Sam's Machine Learning Analysis, Data Structure-Architect©:
Case Study - Autonomous Vehicles©
Sam's Machine Learning Analysis, Data Structure-Architect©
Physical Units:
Any hardware regardless if the hardware is a part of a computer system is a Physical Unit
or a Component. Sadly Oil and Gas Refinery has Hugh number of Physical Units or Components. Our
security architect must include every item so it can be tracked, monitored, audit trail and
secured with its functionalities. We would be using our approaches for cloud system, Data
Center, Autonomous Vehicles or networks. At this point in our analysis, we do need help with
how can we secure every Physical Unit.
Human Factor:
Human Factor is applicable to any system, plus it could be a key to Nemours issues. For example, in
Cybersecurity a Phishing tactic is to lure individuals into providing sensitive data such as personally
ID, passwords, banking and credit card or any information hackers can use to gain system access. We
view Human Factor in Oil and Gas Refinery case totally different since one error could result in
tragedy with human lives are at risk. We believe security preparation or readiness for all possible
events or actions is the big key in prevention. Therefore the following is what we consider to be
security readiness:
1. Written Processes
2. Training
3. Supervisions
4. Automation of Procedures
5. Checkpoints Processes- example, where two or more person would be giving the OK to start
6. Evacuation Procedures and Drills
7. Surveillance Cameras
8. Sensors
9. Rollbacks
10. Emergency Handling and support
11. Quick Shutdown
12. Evacuation Procedures
13. Audit Trail
14. Tracking
15. Listens Learned
In a nutshell, what we should do before the fact and not after things already happened. Plus we
use history as a guideline for learning and preparation.
Mother Nature/Environments:
Security is our goal, therefore any factor including Mother Nature/Environments is a security risk(s) which we need to address.
Providing security processes for Natural events are not our expertise, but we are open to team
up with the experts and build the security processes, software, tools, training, ..etc.
Strategy:
As an architect we always look at the worst case and the best case scenarios. The best
case may not be an ideal in term of Cybersecurity or security in general. Therefore we
are presenting what we consider the worst case Scenario.
Security Worst Case Scenario:
Most Oil and Gas companies are the largest in the world in term of finance and political
influence. For example:
#1 Saudi Arabian Oil Co. ( Saudi Aramco) - Revenue: $590.3 billion.
#2: Sinopec (Chinese Petroleum and Chemicals Corporation) - Revenue: $405.4 Billion
#3: PetroChina 2021 Revenue: $386.86 USD Billion
The worst case would where all the 7 vulnerability (Hazardous Objects, Terrorists Attacks,
Facilities, Operations, Computer System, Communication and Shipping and Ports) are happening in
all the facilities simultaneous.
Our strategy in addressing this case is that we need to look the following and draw some pointers:
1. History of issues and how severe
2. How US Navy handles securing personnel, equipments, ships, sites, camps, ports, ..etc.
3.Pros and Cos of using technologies by the Oil and Gas Companies and their adversaries.
4. What is practical and doable to implement
5. The cost of security
1. History of issues and how severe:
3. Pros and Cos of using technologies by the Oil and Gas Companies and their adversaries:
4. What is practical and doable to implement:
5. The cost of security:
We are a technical team and history or politics are not our expertise and we leave it for Oil
and Gas companies to provide.
2. How US Navy handles securing personnel, equipments, ships, sites, camps, ports, ..etc.
Searching the interest on what are the US Navy strategies for securing personnel, equipments, ships, sites,
camps, ports, ..etc?
We came up with following list:
1. People, Processes, Capabilities
2. Modernize
3. Prioritize
4. Integration
5. Information Management
6. International Partners
7. Budget
We would also like to add the following:
8. Virtualization
9. Automation
10. Intelligence
Oil and Gas are not in the business of conflicts nor defense, but securing personnel, equipments,
ships-ports, sites, oil and gas sites and rigs, ..etc is a must to insure no interruption of business
nor stopping of operations. From our analysis we can state that the biggest issue with Oil and Gas
industries is Hazardous Objects. Therefore security must address Hazardous Objects.
Redefine Security:
At this point we do not look at security as Cybersecurity, but we redefine security as securing
Hazardous Objects, Cybersecurity, Protection Against Piracy, Terrorists Attacks, Theft, Vandalism,
Operations, Shipping and Ports, System Wipe Out, Weather and Storms and Interruption of Service. Plus
Oil and Gas companies may need to use US Navy strategies we mentioned above.
Data (Paperless) Trail, Updates and System Image - Black Box:
Issues at Hands:
We believe the real issues at hand is how to prevent any interruption of service since any interruption
may have deadly consequences or economic disasters. Energy is the center of our daily life and interruptions
of energy have disastrous consequences. For example, all the major hospitals with hundreds of thousands of
patients and operations, cannot offered interruptions in their energy supplies.
Our Concerns and Questions:
These are some of our concerns and questions, but what we are presenting is the start of a long list:
• How to secure the continuation Oil and Gas operations?
• How to monitor personnel, procedures, equipment, computer systems, weather and outsiders?
• How to prevent human negligence or errors from taking place?
• How to reinstall computer system in case of cyber attack where all system were wiped clean?
• How to reinstall data system in case of Ransomware where accessing data is permanently blocked?
• How to monitor and protect pipelines from attacks or Sabotage?
• ... etc.
Black Box Concept:
The Black Box, technically known as Flight Data Recorder, is an instrument that records all the activities
of aircraft during its flight. Black Box is designed to survive any crash and with its valuable data.
Our Black Box:
Our Black Box is an Edge Computing Boxes-System with built-in small size bare-metal servers. Each
bare-metal server runs independently. We had named each bare-metal a "Service Unit". Each has its
own power-battery supply.
Paperless Trail:
It is accustomed in modern businesses to have paper trail as solid record keeping for tracking. In our
case, we do have a Magnetic or Laser Trail of records, where the trail is either magnetic (saved on disk)
or laser (saved on CD). Our Paperless trail is used as a permanent recordkeeping.
Read-Only Data or System Images:
To prevent damaging data or system images or overwrite them, we are proposing Read-Only devices as a part
of the Edge Computing Boxes (servers).
Our Approach:
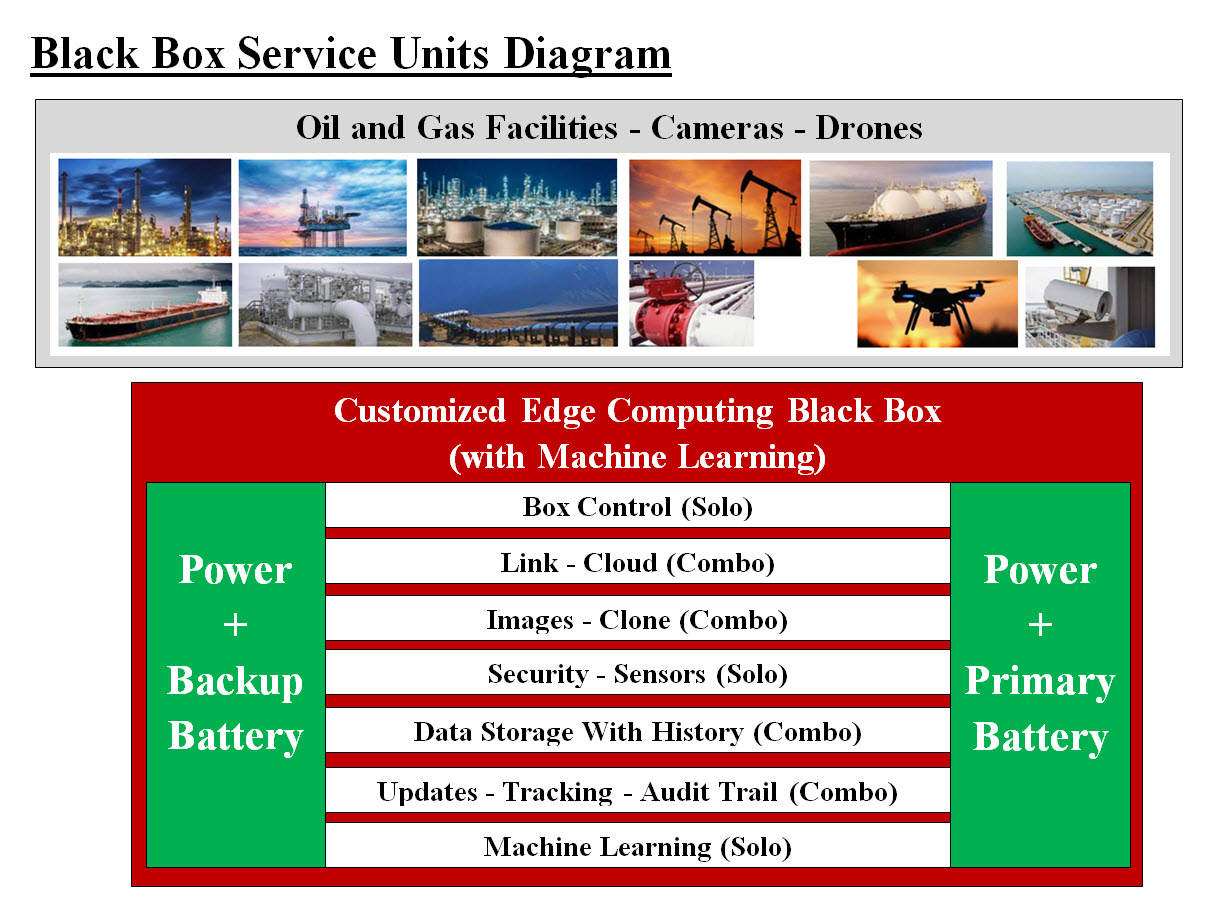
Image #1
Our approach is to create Edge Computing Box with the following capabilities:
1. Intelligent
2. Secured
3. Outside
4. Physically Protected
5. Closed
6. Layered
7. Component-Based
8. Self-Starter
9. Integrate-able
10. Independent
11. Cloud
12. Remotely Controlled
13. Energy Efficient
14. Track-able
15. Machine Learning Tools
Image #1 presents a customized Edge Computing Boxes-System to be used by the Oil and Gas facilities.
Each Edge Computing Box would have a set of "Service Units " (Bare-Metal Servers) based on the needed
functionalities and services.
Service Unit (Bare-Metal Sever) Types:
Solo:
"Solo Service Unit" is a dedicated unit to perform only one task such as Box Control Unit.
Combo:
"Combo Service Unit" performs one or more tasks such as Link-Cloud.
Box Control:
Box Control runs the management system of the entire Edge Computing Boxes-System. It also
follow master-slave concept, where if it fails the another Service Unit would become the
Box Control Unit.
Link-Cloud:
This unit handles both internal and external communication. It is hardwired to all the other service units.
Image-Clone:
Every running system must have its clone object (Image File) which would be used to rebuild the
bare-metal server with all its functionalities. In case of cyber attack which would wipe out or
damage a running system, such Image file would be used to rebuild the bare-metal server. The
rebuilding can be customized to be performed automatically or on demand by the Box Control. Remote
buildup can be also done as an option.
Security-Sensors:
A dedicated server or set of servers would perform all the security functionalities including
monitoring sensors (cameras, radar, equipment sensors, weather, navigation, ..etc). Security-Sensors
would be using Link-Cloud Service Unit to upload all the security data to headquarter for
tracking. Encryption-Compression would be used in such communication.
Data Storage With History:
Any critical data created or used would be written permanently to NAS or Laser disks with a timestamp. Tracking
and updating a Image-Clone server would be using such history of storage to recover to whatever previous
state which seems fit by the system.
Updates-Tracking-Audit Trail:
A set of servers would perform the all Updates-Tracking-Audit Trail and would be using Link-Cloud
Service Unit to upload all the security data to headquarter for tracking. Such data is critical to
Machine Learning Tools and services.
Machine Learning:
We would be using Our Autonomous Vehicle approaches and tools for Machine learning.
Other Services:
Based on whatever needed services there should be a set of servers which would perform the required services.
Power Plus Battery Backup System:
We do need help from the experts with power and Battery Backup System.
Service Units Implementation Table:
|
Vulnerability Type
|
Service Unit Used
|
Comments
|
|
Hazardous Objects
|
Security-Sensors
Updates-Tracking-Audit Trail
Machine Learning
Other Services
|
The key issue about Hazardous Objects is these objects require constant mentoring and prevention using the listed service units.
Machine Learning would support the Pre and Post conditions and processes.
|
|
Terrorists Attacks
|
Security-Sensors
Updates-Tracking-Audit Trail
Machine Learning
Other Services
|
The Service Units listed would have the Pre and the Post conditions and operations to handle any Terrorists Attacks.
Machine Learning would the intelligence needed for the Pre and Post processes.
|
|
Facilities
|
Link-Cloud
Image-Clone
Security-Sensors
Data Storage With History
Updates-Tracking-Audit Trail
Machine Learning
Other Services
|
Facilities need all the help they can get
|
|
Operations
|
Link-Cloud
Image-Clone
Security-Sensors
Data Storage With History
Updates-Tracking-Audit Trail
Machine Learning
Other Services
|
Facilities need all the help they can get
|
|
Computer System
|
Link-Cloud
Image-Clone
Security-Sensors
Data Storage With History
Updates-Tracking-Audit Trail
Machine Learning
Other Services
|
Computer System needs detection, remedy and rollbacks
|
|
Communication
|
Link-Cloud
Image-Clone
Security-Sensors
Data Storage With History
Updates-Tracking-Audit Trail
Machine Learning
Other Services
|
Communication is critical in keeping the facilities, tankers, ports and sites in synchronization with command centers
|
|
Shipping and Ports
|
Link-Cloud
Image-Clone
Security-Sensors
Data Storage With History
Updates-Tracking-Audit Trail
Machine Learning
Other Services
|
Something as Terrorists Attacks, Computer System and Operations.
|
Using Our Autonomous Vehicle (AV) Approaches and Tools:
Our Autonomous Vehicle (AV) Approaches and Tools present a very unique case of Cybersecurity
and physical security which would help with some of analysis-architect-development details in
building our Edge Computing Boxes-System. For example, Autonomous sensors play an essential role
in autonomous vehicles. These sensors allow cars to monitor their surroundings, detect oncoming
obstacles, and safely plan their paths. The intelligence, automation and functionalities of these
sensors can be implemented in the security sensors in our Edge Computing Boxes-System. Plus Using
Computer Models and Virtual Testing for AV can be reused in our Edge Computing Boxes-System
Virtual Testing.
|
|


